Anticoagulation for Mechanical valves
Anticoagulation for Surgical Procedures in patients with Mechanical valves For high risk non-cardiac surgeries in...
Choice of valve prosthesis for mitral valve replacement
Contents1 Mechanical prosthesis is recommended for patients for mitral valve replacement2 Guideline from ACC/AHA in...
Clinical Questions -1
Contents1 What is the indication of Transvaginal ultrasound in this case of Hydatidiform mole ?2...
Image Question-24
Contents1 What is the diagnosis of Image?2 Bunch of Grapes sign3 Bunch of Grapes sign...
Endocrinology in Relation to Reproduction
Contents1 Corpus luteum of pregnancy secretes all except2 Which cell organelle is abundantly present in...
Metabolic Adaptations in Pregnancy
Contents1 All are true of carbohydrate metabolism in pregnancy except2 Not true of physiological changes...
The fetal membranes
Contents1 What describes chorion best2 Not a function of Amniotic fluid3 Not a feature of...
Mitral Valve – Surgical Considerations
Contents1 Stiffness of the valve decreases in the presence of –2 ALL are TRUE about...
The Placenta
Contents1 Thickness of placenta increases up to2 Not true of placenta3 Not a part of...
Ovarian Failure
Contents1 The most common genetic form of premature ovarian insufficiency ( POI) is2 Anti-ovarian antibodies...
What are the types of homocystinuria?
What are the types of homocystinuria? Homocystinuria type-I- Due to the deficiency of cystathionine ß…
Medicine MCQs-4
Presence of splenomegaly in a patient with polycythemia supports a diagnosis of -
Presence of splenomegaly supports a diagnosis of polycythemia vera rather than secondary polycythemia.
All of the following are adaptive functions of normal human Spleen EXCEPT -
Adaptive unctions of Spleen :
(1) Clearance of bacteria and particulates from the blood,
(2) Immune responses to pathogens,
(3) Extramedullary hematopoiesis
Normal human spleen does not sequester or store red blood cells and does not contract in response to sympathetic stimuli.
Presence of a palpable spleen in a patient with sickle cell disease after age 5 suggests -
Presence of a palpable spleen in a patient with sickle cell disease after age 5 suggests a coexisting hemoglobinopathy, e.g., thalassemia or hemoglobin C
Philadelphia Chromosome is seen in -
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has a presence of the hallmark Philadelphia Chromosome (BCR-ABL1) mutation.
Castell's sign is a medical sign assessed to evaluate -
Castell's sign is a medical sign assessed to evaluate splenomegaly
Microcytosis is reflected by MCV -
Microcytosis - MCV < 80
Macrocytosis. - MCV >100
All of the following are associated with massive splenomegaly EXCEPT -
DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH MASSIVE SPLENOMEGALY -
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- Gaucher’s disease
- Lymphomas
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Hairy cell leukemia
- Sarcoidosis
- Polycythemia vera
Sickle cell anemia - autosplenectomy
Pneumococcal sepsis- has been reported to cause autosplenectomy but is a very rare
Signs of hypovolemic shock appears when acute blood loss is -
Volume of acute blood lost is >40% [ i.e.,>2L in the average-sized adult ] signs of hypo-volemic shock appears
All of the following are classified as myloproliferative neoplasms EXCEPT -
World Health Organization lists the following subcategories of MPNs:
• Chronic myeloid leukemia
• Chronic neutrophilic leukemia
• Polycythemia vera
• Primary myelofibrosis
• PMF, Prefibrotic Stage
• PMF, Overt Fibrotic Stage
• Essential thrombocythemia
• Chronic eosinophilic leukemia
Previously, myloproliferative neoplasms were known as myeloproliferative diseases
Gaisbock’s syndrome is best categorized under the heading of -
Gaisbock’s syndrome is best categorized under the heading of a relative polycythemia
Medicine MCQs – 3
Which is the most frequently detected “atypical” organism in community-acquired pneumonia in adults?
Community-acquired pneumonia in adults - M. pneumoniae is the most frequently detected “atypical” organism.
Brill-Zinsser disease is a type of -
Brill–Zinsser disease :
- relapse of epidemic typhus, caused by Rickettsia prowazekii.
- Brill-Zinsser disease is an exacerbation of epidemic louse-borne typhus fever.
- Caused by Rickettsia prowazekii.
- Rather than being eradicated, the microorganisms become latent and reappear after several years as a milder form of the disease.
Which of the following is the most frequently reported travel-associated rickettsial infections?
Tickborne spotted fever rickettsioses are the most frequently reported travel-associated rickettsial infections.
Which is called as 'walking pneumonia' ?
Walking pneumonia
"Primary atypical pneumonia" is called primary because it develops independently of other diseases.
Known as "walking pneumonia" because its symptoms are often mild enough that one can still work and walk.
How addition of hydroxychloroquine to doxycycline for treatment against C. burnetii helps?
Addition of hydroxychloroquine to doxycycline against C. burnetii helps to - alkalinize the phagolysosome
Hydroxychloroquine increases lysosomal pH in antigen-presenting cells by two mechanisms: As a weak base, it is a proton acceptor and via this chemical interaction, its accumulation in lysozymes raises the intralysosomal pH
C. burnetii escapes intracellular killing in macrophages by inhibition of -
C. burnetii
- gram-negative cell wall,
- survives in harsh environments
- escapes intracellular killing in macrophages by inhibiting the final step in phagosome maturation (cathepsin fusion)
- has adapted to the acidic phagolysosome by producing superoxide dismutase
What is the causative agent of rickettsialpox?
causative agent of rickettsialpox - R. akari
All of the following are characteristic lab finding of rickettsioses EXCEPT -
Characteristic laboratory findings -
- Thrombocytopenia
- Normal or low white blood cell [WBC] counts, elevated hepatic enzyme levels
- Hyponatremia
What is the drug of choice of rocky mountain spotted fever in pregnant patients
Drug of choice for the treatment of both children and adults with rocky mountain spotted fever is doxycycline, except when the patient is pregnant
Pregnancy - Treatment with chloramphenicol, a less effective drug, is advised only for patients who are pregnant
Which is the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia
Medicine MCQs – 2
Low-FODMAP diet is used for -
Dietary modification to reduce the volume of flatus produced is - reducing the amount of fermentable carbohydrates.
Low-FODMAP diet- low fermentable oligosaccharide, disacharide, monosaccharide and polyols
Bilateral renal cell carcinomas is seen in -
von Hippel–Lindau disease -
- autosomal dominant disorder We can find - - bilateral renal cell carcinomas - haemangioblastomas - phaeochromocytomas - renal cysts
VHL syndrome is found in 4.3% of bilateral RCCs
Café au lait spots with rough borders seen in -
Café au lait spots are often harmless but may be associated with syndromes such as neurofibromatosis type 1 and McCune–Albright syndrome
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 -
- Café au lait lesions tend to resemble the "coast of California," rather than the "coast of Maine," - Meaning the edges are smoother and more linear.
McCune-Albright syndrome.- Café au lait lesions with rough borders (“coast of Maine”)
Most common form of glomerulonephritis in adults worldwide -
IgA nephropathy is also known as Berger's disease. It is the most common form of glomerulonephritis in adults worldwide
IgA nephropathy, also known as Berger's disease, is the most common type of glomerulonephritis, and generally presents with isolated visible or occult hematuria, occasionally combined with low grade proteinuria
Check shoulder shrug or trapezius muscle action is the testing of which nerve -
CN XI (Spinal Accessory) Check shoulder shrug (trapezius muscle) and head rotation to each side (sternocleidomastoid) against resistance.
All of the following are usually CORRECT about Isolated proteinuria without hematuria EXCEPT -
Isolated proteinuria without hematuria
is usually in the sub-nephrotic range without an active urine sediment and there is normal renal function. Over 50% of these patients have postural proteinuria.
Most common form of electrolyte disorder in the emergency room
Hyponatremia is the most common form of electrolyte disorder in the emergency room
Early-morning nausea and vomiting is seen in all of the following cases EXCEPT -
Early-morning nausea and vomiting is seen in -
- Pregnancy
- Alcohol dependence
- Uraemia.
Large volumes of vomit - suggest gastric outlet or upper intestinal obstruction.
Horizontal nystagmus is best assessed at -
Horizontal nystagmus is best assessed at 45° and not at extreme lateral gaze
Patients with aerophagia have excessive intestinal gas that is mostly composed of -
Patients who have excessive intestinal gas that is mostly composed of nitrogen have aerophagia
Café au lait spots
Café au lait spots are often harmless but may be associated with syndromes such as…
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia – when calcium concentration is >14 mg/dL, individuals may experience confusion, altered mental status, coma,…
Acetaminophen & Hepatic injury
Blood levels of acetaminophen correlate with severity of hepatic injury levels >300 μg/mL 4 h…
Medicine MCQs -1
When both parents are carriers for Tay–Sachs disease there is how much % risk of giving birth to an affected child with each pregnancy?
Tay–Sachs disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder- when both parents are carriers, there is a 25% risk of giving birth to an affected child with each pregnancy
Jordans anomaly shows persistent vacuolation of -
Jordans anomaly [Jordans bodies]- persistent vacuolation of granulocytes and monocytes in the peripheral blood and bone marrow.
ordans' anomaly is a characteristic finding in Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome and other neutral lipid storage diseases.
Associated with mutations in the PNPLA2 gene
Tay–Sachs disease becomes apparent almost always by which month of life?
Tay–Sachs disease - disease becomes apparent in the first weeks and months of life, almost always by the fourth month
Cherry-red spot at macula is seen in all of the following cases EXCEPT -
Cherry-red spot at macula in Metabolic Storage Diseases:
Tay–Sachs disease
Farber disease
GM1 and GM2 gangliosidoses
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
Niemann–Pick disease
Sandhoff disease
Sialidosis
Sea-blue histiocytes are seen in all of the following EXCEPT-
Sea-blue histiocytes is a secondary finding associated with -
myelodysplastic syndromes,
lymphomas,
chronic myelogenous leukemia,
idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura,
Niemann-Pick disease,
Norum disease
Sea-Blue histiocytosis
Synonyms
Inherited Lipemic Splenomegaly
Histiocytosis, sea-blue
Sea-Blue histiocyte disease
Patient presented with clinical symptoms include bleeding problems and on examination found to have hepatosplenomegaly blood parameters shows thrombocytopenia, elevated bile acid with normal bilirubin, and mildly prolonged prothrombin time and elevated concentrations of ribitol, arabitol, and erythritol in urine sample. Which of the following is the possibility?
Transaldolase (TALDO) Deficiency
Clinical symptoms include-
Bleeding problems, hepatosplenomegaly, liver cirrhosis, thrombocytopenia, elevated bile acid with normal bilirubin, and mildly prolonged prothrombin time
The deficiency of TALDO enzyme is diagnosed by elevated concentrations of ribitol, arabitol, and erythritol in urine sample.
PGL4 syndrome is caused by mutation of -
PGL4 syndrome - due to SDHB mutations
SDHB gene provides instructions for making one of four subunits of the succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) enzyme.
Tay–Sachs disease is caused by a genetic mutation in -
Hexosaminidase A (alpha polypeptide)[ HEXA] is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HEXA gene, located on the 15th chromosome.
Tay–Sachs disease is caused by a genetic mutation in the HEXA gene
Which of the following is called as Vanishing white matter disease-
Vanishing white matter disease-
Childhood ataxia with central hypomyelination (CACH),
Genetic leukoencephalopathy due to mutations in EIF2B subunit mutations,
Extensive white matter involvement with cavitary changes.
Tay–Sachs disease is caused by insufficient activity of the enzyme -
Tay–Sachs disease is caused by insufficient activity of the enzyme hexosaminidase A
Krabbe disease is caused by-
mutations in the
GALC gene located on chromosome 14
Autosomal recessive
Mutations in the GALC gene cause a deficiency of an enzyme called galactosylceramidase.
Mutations in the SMPD1 gene cause Niemann–Pick disease types A and B.
They produce a deficiency in the activity of the lysosomal enzyme acid sphingomyelinase which breaks down the lipid sphingomyelin
Taxonomy
Heart Failure -I
What is the commonest cause of heart failure?
Ischaemic heart disease - 35–40%
Cardiomyopathy (dilated) - 30–34% Hypertension - 15–20%
Weight loss of 4.5 kg in ............ days in response to treatment is a Framingham major criteria.
The Framingham criteria for the diagnosis of heart failure consists of the concurrent presence of either two major criteria or one major and two minor criteria.
Major criteria comprise the following:
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
Weight loss of 4.5 kg in 5 days in response to treatment
Neck vein distention
Rales
Acute pulmonary edema
Hepatojugular reflux
S 3 gallop
Central venous pressure greater than 16 cm water
Circulation time of 25 seconds or longer
Radiographic cardiomegaly
Pulmonary edema, visceral congestion, or cardiomegaly at autopsy
Minor criteria (accepted only if they cannot be attributed to another medical condition) are as follows:
Nocturnal cough
Dyspnea on ordinary exertion
A decrease in vital capacity by one third the maximal value recorded
Pleural effusion
Tachycardia (rate of 120 bpm)
Hepatomegaly
Bilateral ankle edema
Licorice can worsen heart failure by -
Licorice can worsen heart failure by increasing blood pressure and promoting fluid retention.
Yohimbine can exacerbate heart failure by increasing blood pressure through -
Yohimbine can exacerbate heart failure by increasing blood pressure through alpha-2 adrenergic receptor antagonism
Which of the following stages of heart failure the patient belongs to when the patient has structural heart disorder, but no symptoms at any stage?
Stage A: People at high risk for developing HF in the future, but no functional or structural heart disorder Stage B: A structural heart disorder, but no symptoms at any stage Stage C: Previous or current symptoms of heart failure in the context of an underlying structural heart problem, but managed with medical treatment Stage D: Advanced disease requiring hospital-based support, a heart transplant, or palliative care
Heart failure cells are -
Heart failure cells are siderophages generated in the alveoli of the lungs of people with left heart failure or chronic pulmonary edema
Patients who achieve at least............. MET-minutes/week had lower heart failure
Recommended minimum by U.S. guidelines -
Patients who achieve at least 500 MET-minutes/week had lower heart failure
Which of the following should be used in those patients who still have symptoms while on an ACE-I or ARB, beta blocker, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist?
Sacubitril/valsartan should be used in those who still have symptoms while on an ACE-I or ARB, beta blocker, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist as it reduces the risks of cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization for heart failure by a further 4.7% (absolute risk reduction).
All of the following is used for risk Stratification in heart failure EXCEPT?
Framingham criteria for the diagnosis of heart failure
Tolvaptan antagonises which of the following receptor?
VAPTANS
Unselective (mixed V1A/V2)
Conivaptan
V1A selective (V1RA)
Relcovaptan
V1B selective (V3RA)
Nelivaptan
V2 selective (V2RA)
Lixivaptan
Mozavaptan
Satavaptan
Tolvaptan
Atrial fibrillation occurs in approximately ------------% of patients with heart failure.
Atrial fibrillation occurs in approximately 20% of patients with heart failure and causes further impairment of cardiac function
Medicine Review MCQs-XVI
Which of the following is Naturally occurring cysteine-rich antibacterial and antifungal polypeptides?
Defensins are naturally occurring cysteine-rich antibacterial and antifungal polypeptides
- 29–35 amino acids
Mast cells share features in common with which of the following cell?
Mast cells share features in common with - Basophils
- Histamine-containing granules
- High-affinity receptors for immunoglobulin E
All of the following are TRUE about Histamine EXCEPT -
Histamine - constitutes 10% of the mast cell’s weight
IgM is a useful diagnostic test for -
- IgM is a useful diagnostic test for recent infection.
- IgG dominates in the second exposure to antigen
CD4+ T cells also known as -
T helper cells-
- assist other lymphocytes, including maturation of B cells into plasma cells and memory B cells,
- activation of cytotoxic T cells and macrophages.
- These cells are also known as CD4+ T cells as they express the CD4 glycoprotein on their surfaces.
IgA2 concentration are higher in -
IgA exists in two isotypes, IgA1 and IgA2.
They are both heavily glycosylated proteins.
While IgA1 predominates in serum (~80%),
IgA2 percentages are higher in secretions than in serum (~35% in secretions)
Which of the following vasculitis caused by deposits of IgA?
Henoch–Schönlein purpura - Known as IgA vasculitis - is a disease of the skin, mucous membranes
All of the following are vasculitis where mostly small vessels are affected EXCEPT -
According to the size of the vessel affected, vasculitis can be classified into:
- Large vessel: Takayasu's arteritis, Temporal arteritis
- Medium vessel: Buerger's disease, Kawasaki disease, Polyarteritis nodosa
- Small vessel: Behçet's syndrome, Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Cutaneous vasculitis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Henoch–Schönlein purpura, and microscopic polyangiitis.
Which is the most commonly implicated drug in causing Linear IgA bullous dermatosis?
Most commonly implicated drug - Vancomycin
All of the following are TRUE Light-chain multiple myeloma EXCEPT -
Light-chain multiple myeloma is a less frequent type of multiple myeloma with a more aggressive course and poorer prognosis.
It is characterized by the inability of the malignant plasma cells to produce heavy chains, resulting in the exclusive production of light chains. Therefore, no M-spike is visible in serum protein electrophoresis.
Exclusive production of light chains No M-spike is visible in serum protein electrophoresis.
Hematology MCQs-I
Criteria for AMML is confirmed if the myleoblasts and promonocytes in the bone marrow are greater than ?
Criteria for AMML is confirmed if the myleoblasts and promonocytes in the bone marrow are greater than 20 percent.
All of the following are TRUE about AML EXCEPT -
AML is slightly more common in men, with a male-to-female ratio of 1.3:1
Acute promyelocytic leukemia has the highest curability
Auer rods are seen in -
Auer rods [also called Auer bodies] - are large, crystalline cytoplasmic inclusion bodies observed in myeloid blast cells -
- acute myeloid leukemia,
- acute promyelocytic leukemia,
- high-grade myelodysplastic syndromes
- myeloproliferative disorders.
Which cytogenetic abnormalities in pediatric and adult B-ALL shows favorable prognosis?
Hyperdiploidy (>50 chromosomes) in B-ALL Shows Favorable prognosis
Which is the commonest malignancy in pediatrics age group?
Most common types of cancer are leukemias, followed by brain and other CNS tumors, lymphomas, neuroblastoma, kidney tumors
Leukemias, which are cancers of the bone marrow and blood, are the most common childhood cancers. They account for about 28% of all cancers in children. The most common types in children are acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
Which is TRUE for Philadelphia chromosome EXCEPT ?
All cases of CML are positive for BCR-ABL1
Fusion gene BCR-ABL1 - coding for a hybrid protein: a tyrosine kinase signalling protein that is "always on", causing the cell to divide uncontrollably by interrupting the stability of the genome and impairing various signaling pathways governing the cell cycle.
Blast crisis in CML is diagnosed if -
Blast crisis in CML is diagnosed if -
>20% blasts in the blood or bone marrow
The presence of an extramedullary proliferation of blasts
What is the test of choice in adults to distinguish CML from Leukemoid reaction?
Philadelphia chromosome is translocation between chromosomes -
Philadelphia chromosome -Ph1 (a reciprocal translocation of chromosomal material between chromosomes 9 and 22)
BCR/ABL mutation
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is considered as a riskfactor of -
Both the hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
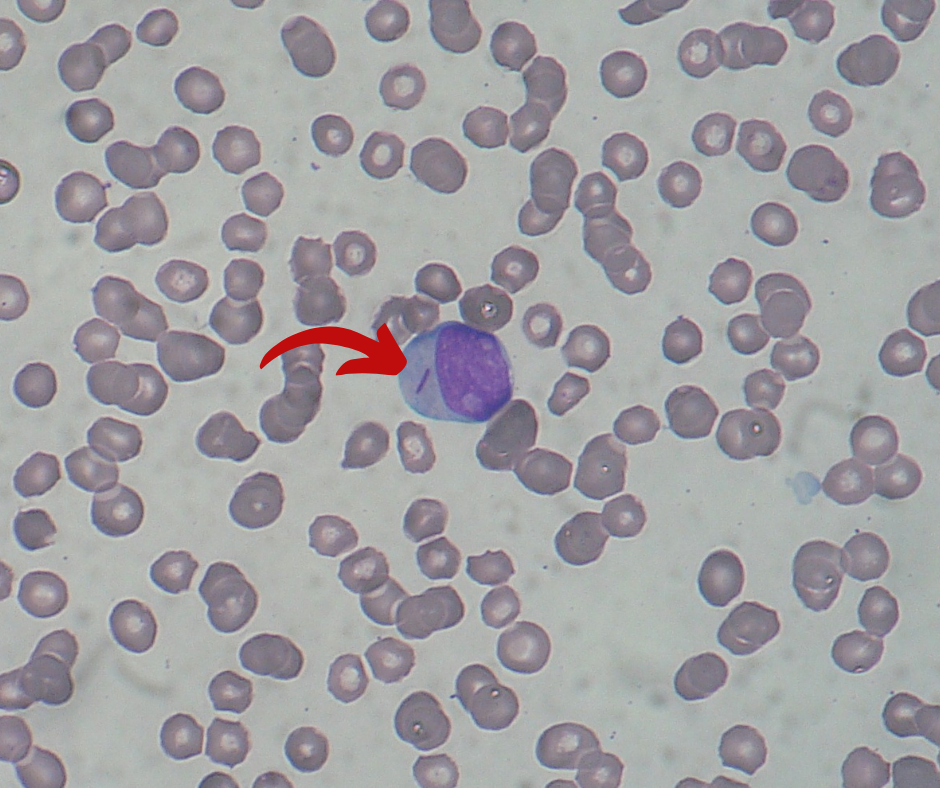
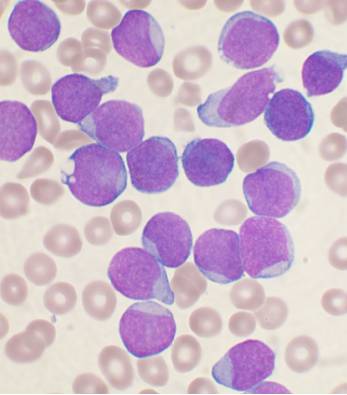
Image Question-12
Analyzing profile ...
What is the Probable diagnosis of the slide?

Please login with Facebook to see your result
Image Question-14



Analyzing profile ...
What is the Probable diagnosis of the slide?

Please login with Facebook to see your result
Share your Results:
Medicine Review MCQs-XV
Which is the richest food source of Vitamin A?
Vitamin A
The richest food source is liver,
Also found in milk, butter, cheese, egg yolks and fish oils.
Beta-carotene is the main carotenoid found in green vegetables, carrots and other yellow and red fruits.
Other carotenoids, lycopene and lutein,
All of the following are unoxygenated (oxygen free) carotenoids EXCEPT ?
Carotenoids with molecules containing oxygen, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, are known as xanthophylls
The unoxygenated (oxygen free) carotenoids such as α-carotene, β-carotene, and lycopene, are known as carotenes. Carotenes typically contain only carbon and hydrogen (i.e., are hydrocarbons),
Which is the most common form of vitamin -B12 used in dietary supplements
Cyanocobalamin is the most common form used in dietary supplements and food fortification because cyanide stabilizes the molecule against degradation.
Which of the following is given in cyanide poisoning?
Hydroxocobalamin
Injected intravenously for the purpose of treating cyanide poisoning, as the hydroxyl group is displaced by cyanide, creating a non-toxic cyanocobalamin that is excreted in urine.
Pernicious anemia characterised by the presence of antibodies to ?
Pernicious anemia-
characterised by stomach atrophy and the presence of antibodies to parietal cells and intrinsic factor
Which is TRUE regarding autoantibodies in Pernicious anemia?
Around 85% of PA patients have parietal cell antibodies, which means they are a sensitive marker for the disease.
Intrinsic factor antibodies are much less sensitive than parietal cell antibodies, but they are much more specific.
Increase in blood levels of Methylmalonic acid and Homocysteine suggests?
Methylmalonic acid and homocysteine - metabolic products that can be measured in the blood.
Increase in the levels of both helps differentiate between vitamin B12 deficiency and folic acid deficiency.
homocysteine alone increases in the Folic acid deficiency.
Which of the following is false for Pernicious anemia?
H. pylori and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome may also cause a form of nonautoimmune gastritis that can lead to pernicious anemia
Diphyllobothrium latum causes --------------- deficiency in humans
Diphyllobothrium latum causes B12 deficiency in humans. >br> Diphyllobothrium latum absorbs around 80% of dietary B12
Administration of which anesthesia can precipitate subacute combined degeneration in people with subclinical vitamin B12 deficiency?
Through oxidation, nitrous oxide inactivates vitamin B12.
In its inactive form, vitamin B12 is unable to function as a co-factor for methionine synthase and methylmalonyl coA mutase.
Methionine synthase converts homocysteine into methionine, which is necessary for the production of myelin proteins, while also converting 5-methyl-tetrahydrofolate into tetrahydrofolate, which is necessary for DNA synthesis.