Hypothalamo Pituitary Ovarian Axis
Contents1 True about Hypothalamo Pituitary Ovarian Axis is2 Most common group II ovulatory disorder is3...
Mitral Valve Anatomy
Contents1 Mechanical and metabolic balance of the valve is maintained by2 Mitral annulus is thinnest...
Carvallo’s sign
Contents1 Carvallo’s sign is a clinical sign found in patients with2 Following is TRUE about...
Ovarian Steroidogenesis
Contents1 Ovarian steroids are produced from all except2 Granulosa cells produce all except3 All are...
Anterior Pituitary gland in reproduction
Contents1 The pituitary gland is primarily derived from2 Not true of pituitary gland cells3 Which...
Dynamic outflow obstruction in HOCM
Contents1 Dynamic outflow obstruction in HOCM is due to2 Asymmetric left ventricular hypertrophy most commonly...
Light-near dissociation
Contents1 Pretectal lesions may be associated with any of 3 different patterns of pupillary deficit.2...
Collier’s sign
Contents1 Collier’s sign also known as –2 Collier’s sign is a medical sign of3 All of the...
Addison’s Plane
Anteriorly it passes through the tip of the 9th costal cartilage Posteriorly through the lower...
Image Question-23
Contents1 What is the diagnosis of Image?2 What is the diagnosis of histopathological slide?3 Gamna-Gandy...
Image Question-15
Analyzing profile ...
What is the Likely Diagnosis?
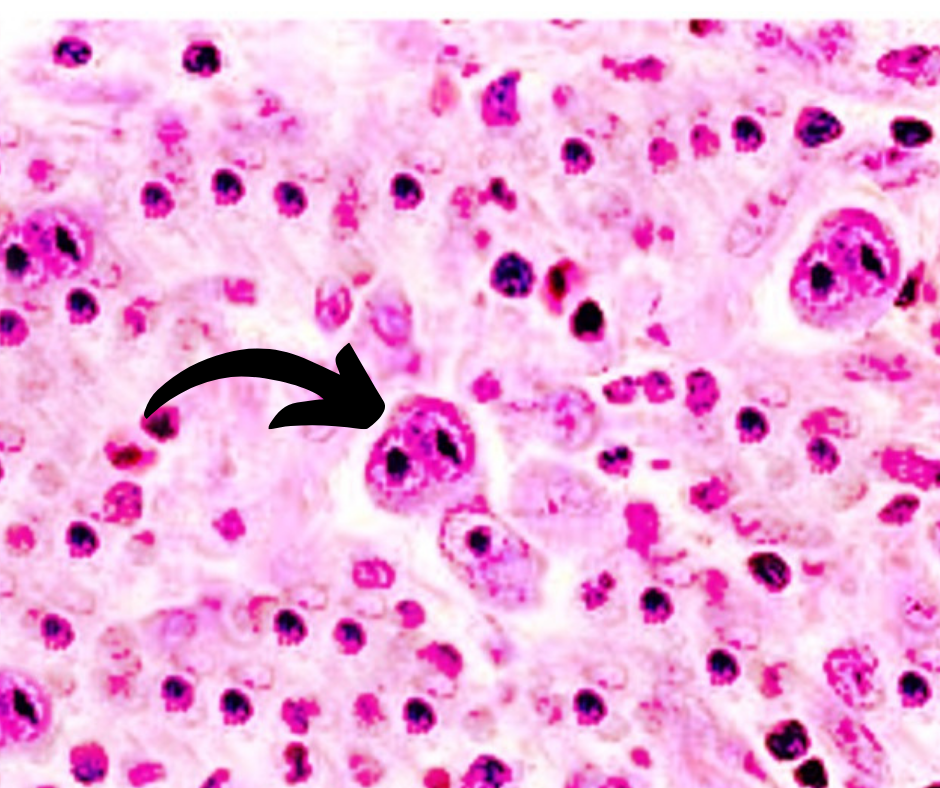 Image Courtesy S Bhimji MD
Image Courtesy S Bhimji MD
Please login with Facebook to see your result
Medicine Review MCQs-XIV
Microscopy of a patient blood smear shows Slightly larger RBCs with Grey blue colour on Gimsa stain preparation. what are those cells?
Poikilocytosis is the term for abnormally shaped red blood cells in the blood. Poikilocytes may be flat, elongated, teardrop-shaped, crescent-shaped, sickle-shaped, or may have pointy projections, or other abnormal features.
Polychromasia is a disorder where there is an abnormally high number of immature red blood cells found in the bloodstream as a result of being prematurely released from the bone marrow during blood formation.These cells are often shades of grayish-blue.
Codocytes are most commonly seen in -
Target cells are also called codocytes.
Codocytes-Most commonly seen in thalassemia, which are due to impaired production of hemoglobin (Hb).
Image shows Supravital stain of a smear of human blood from a patient with hemolytic anemia. What is the cell marked by arrow?
 By Ed Uthman, MD, pathologist, Houston, Texas, USA - Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=12209264
By Ed Uthman, MD, pathologist, Houston, Texas, USA - Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=12209264
Supravital stain of a smear of human blood :
From a patient with hemolytic anemia.
The reticulocytes are the cells with the dark blue dots and curved linear structures (reticulum) in the cytoplasm.
Hereditary spherocytosis is most commonly due to mutations in genes that code for -
spectrin (alpha and beta), ankyrin, band 3 protein, protein 4.2
Hereditary Spherocytosis autosomal recessive inheritance usually account for -
Recessive inheritance may account for 20-25% of all HS cases
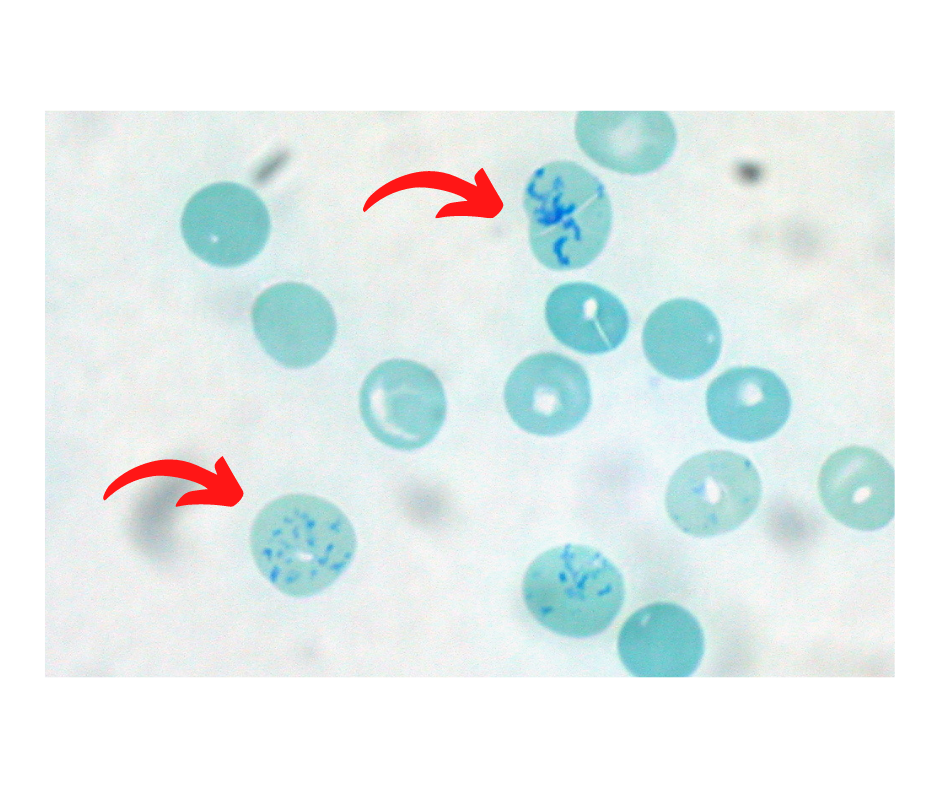
Which is the condition where cell marked in the IMAGE is seen most commonly ?
 By Dr Graham Beards - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=20526635
By Dr Graham Beards - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=20526635
Target cells (codocytes): Most commonly seen in thalassemia.
Normal Hb has two alpha, and two beta chains, a decrease in alpha chains is alpha thalassemia, a decrease in beta chains is beta-thalassemia.
Target cells appear in association with the following conditions: Liver disease: Lecithin—cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) activity may be decreased in obstructive liver disease. Alpha-thalassemia and beta-thalassemia Hemoglobin C Disease Iron deficiency anemia Post-splenectomy Autosplenectomy
Amino acid substitution of lysine for glutamic acid at position six of the beta hemoglobin chain results in which of the following?
Hemoglobin S- coding of valine instead of glutamate in position 6 of the hemoglobin beta chain
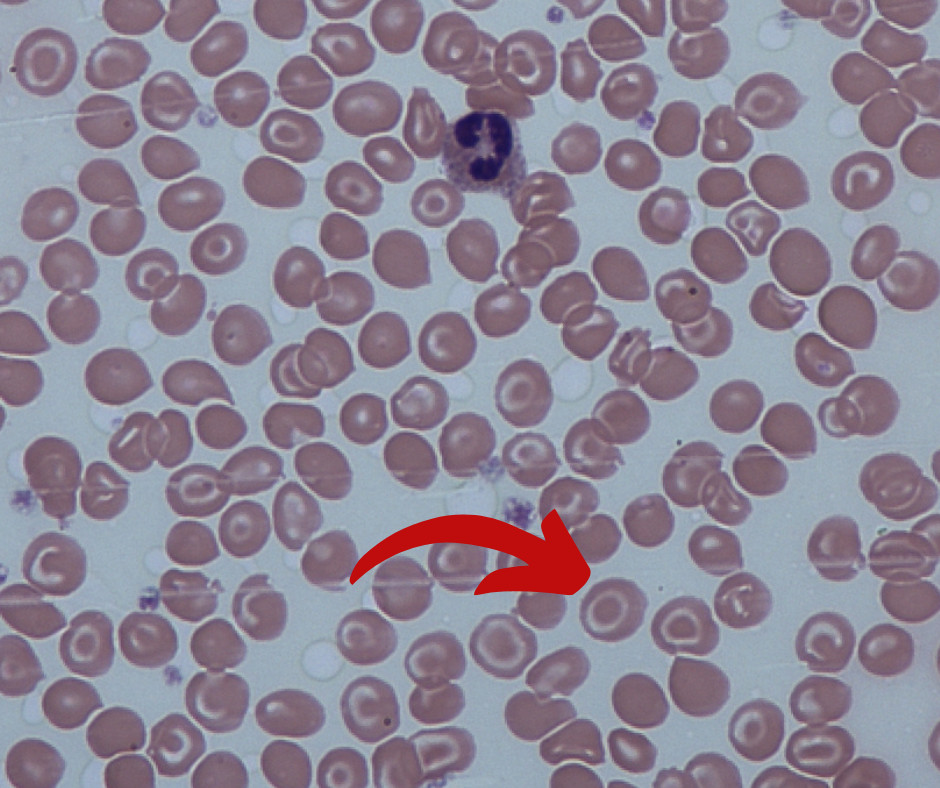
Howell–Jolly body are seen in most commonly which of the following condition ?
Howell–Jolly body is a cytopathological finding of basophilic nuclear remnants (clusters of DNA) in circulating erythrocytes
Spleens are also removed for therapeutic purposes in conditions like hereditary spherocytosis, trauma to the spleen, and autosplenectomy caused by sickle cell anemia.
Myelodysplastic syndrome can transform into which of the following?
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) often transforms into acute myeloid leukemia [AML].
Transformation of MDS into acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is extremely rare.
In Myelodysplastic syndrome if Bone-marrow myeloblasts rises over ---------% it is considered transformation to acute myelogenous leukemia [WHO] ?
Overall percentage of bone-marrow myeloblasts rises over a particular cutoff (20% for WHO and 30% for FAB), then transformation to acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) is said to have occurred.
Reticulocyte index for a healthy individual should be in range?
Reticulocyte index (RI) should be between 0.5% and 2.5% for a healthy individual.
Medicine Review MCQs-XIII
All of the following are CORRECT for Bernard–Soulier syndrome EXCEPT -
Bernard–Soulier syndrome
Low platelet count
Bernard–Soulier syndrome -caused by a deficiency of the glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex (GPIb-IX-V), the receptor for von Willebrand factor
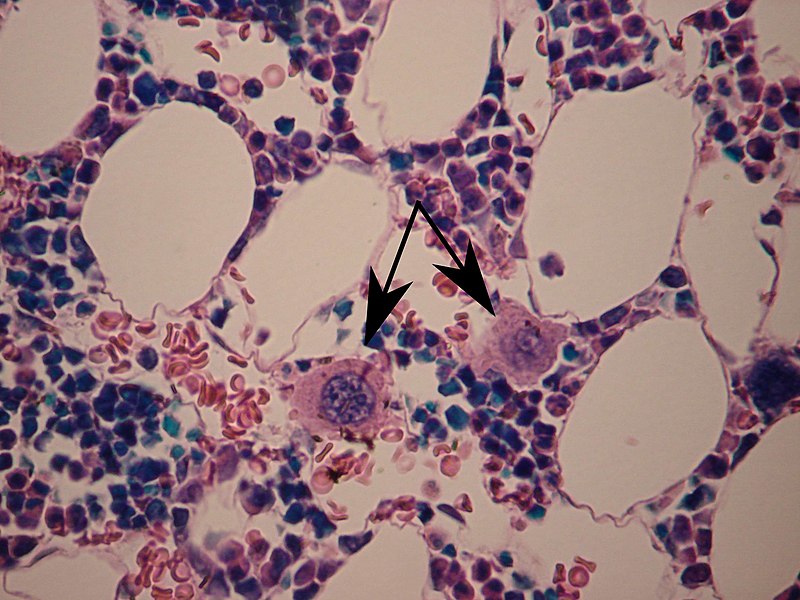
What is the Marked structure in Image?
 By WVSOM_Megakaryocytes.JPG: Wbensmithderivative work: Icewalker cs (talk) - WVSOM_Megakaryocytes.JPG, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=15216382 - Medicine Question Bank
By WVSOM_Megakaryocytes.JPG: Wbensmithderivative work: Icewalker cs (talk) - WVSOM_Megakaryocytes.JPG, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=15216382 - Medicine Question Bank
Megakaryocytes in bone marrow -marked with arrows
Platelet-producing megakaryocytes go through ................during cell differentiation
Platelet-producing megakaryocytes go through endomitosis during cell differentiation
Megakaryocytes are derived from ................... stem cell
Megakaryocytes are derived from hematopoietic stem cell precursor cells in the bone marrow. They are produced primarily by the liver, kidney, spleen, and bone marrow.
The primary signal for megakaryocyte production is -
The primary signal for megakaryocyte production is thrombopoietin
sufficient but not absolutely necessary for inducing differentiation of progenitor cells in the bone marrow towards a final megakaryocyte phenotype.
All of the following include Lymphoid cells EXCEPT -
Lymphoid cells include T cells, B cells, natural killer cells, and innate lymphoid cells.
Clock Face Nucleus seen in -
Plasma cell nucleus - cartwheel or clock face arrangement
Reed-Sternberg cells seen in -
Hodgkin lymphoma characteristically presents with Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells.
When the cells are mononucleated, they are called Hodgkin cells.
When they are multinucleated, they are called Reed-Sternberg cells.
Owl’s Eye Appearance nucleus seen in -
Owl's eye appearance of the Lentiform nucleus of the basal ganglia seen on head CT scan images of patients with -
Cerebral hypoxia
Medicine Review MCQs -XII
Asbestosis can cause all of the following EXCEPT -
Asbestosis can cause - Lung cancer, Mesothelioma, and Pulmonary heart disease.
More than ------- % of people affected with asbestosis develop plaques in the parietal pleura
>50%
The commonest manifestation of asbestos exposure is pleural disease, including pleural plaques and diffuse pleural thickening (DPT). Malignant mesothelioma of the pleura and DPT are less common than plaques,
Which of the following patients are particularly susceptible to tuberculosis
Patients with silicosis are particularly susceptible to tuberculosis
Chalicosis is a form of pneumoconiosis caused by the inhalation of fine particles of stone -
Chalicosis is a form of pneumoconiosis affecting the lungs or bronchioles, found chiefly among
Ferruginous body is a histopathologic finding in interstitial lung disease suggestive of ?
Ferruginous body is a histopathologic finding in interstitial lung disease suggestive of - Asbestosis
Ferruginous body - appear as small brown nodules in the septum of the alveolus. Ferruginous bodies are typically indicative of asbestos inhalation (when the presence of asbestos is verified they are called "asbestos bodies")
Caplan's syndrome is a combination of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with -
Caplan's syndrome is a combination of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with Pneumoconiosis
Anthracosis a form of
Coal workers' pneumoconiosis, severe state, develops after the initial, milder form of the disease known as anthracosis
Anthracosis - Asymptomatic and is found to at least some extent in all urban dwellers due to air pollution.
Asbestosis causes all EXCEPT -
As the fibrosis progresses, a number of more definite findings are seen, which continue to be particularly subpleural and lower lung zone in distribution. They include:
-parenchymal bands
-traction bronchiectasis
-honeycomb fibrosis
In which of the following pleural plaques are pathognomonic on X-ray?
Pleural plaques are pathognomonic on X-ray - Asbestosis
All of the following are found in Silicosis EXCEPT -
Ferruginous body - Small brown nodules in the septum of the alveolus
What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis of X-RAY?
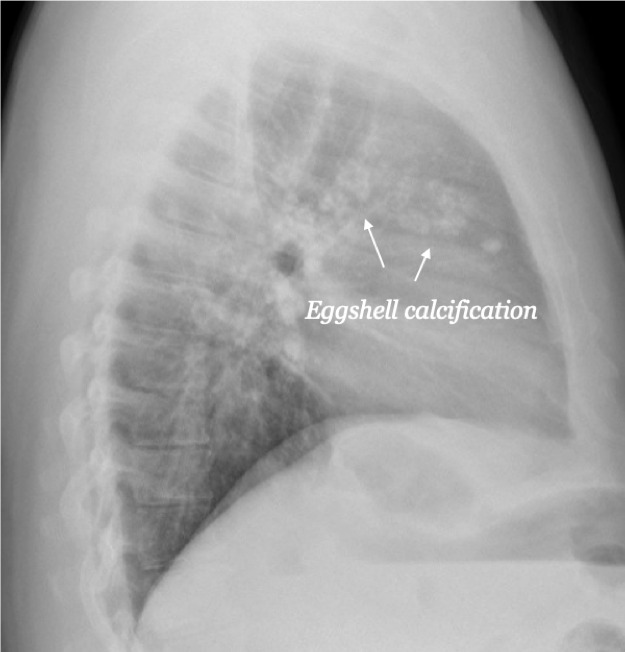
Silicosis - Egg shell calcification
Ferruginous body are found in which anatomical location?
Ferruginous body -Small brown nodules in the septum of the alveolus
Medicine Review MCQs -XI
The drug of choice of cryptococcal meningitis -
[AI -1995]
Induction therapy - Amphotericin B
Tropical spastic paraparesis is caused by -
[AIIMS -2015]
Tropical spastic paraparesis - causes weakness, muscle spasms, and sensory disturbance
Causative agent - Human T-lymphotropic virus [HTLV] resulting in paraparesis
All of the following are TRUE about Ramsay hunt syndrome EXCEPT -
Palatal myoclonus is a rapid spasm of the palatal (roof of the mouth) muscles - due to lesions of the central tegmental tract (which connects the red nucleus to the ipsilateral inferior olivary nucleus). Uniquely, the clicking noise does not subside when the patient sleeps.
All of the following are TRUE about Palatal Myoclonus EXCEPT -
Palatal myoclonus-
Rapid spasm of the palatal (roof of the mouth) muscles, which results in clicking or popping in the ear.
Movements of the palate vary in rate between 40 and 200 beats per minute.
Chronic clonus is often due to lesions of the central tegmental tract (which connects the red nucleus to the ipsilateral inferior olivary nucleus).
Uniquely, the clicking noise does not subside when the patient sleeps.
CSF glucose level is approximately ---------- of Plasma glucose
The glucose level in CSF is proportional to the blood glucose level and corresponds to 60-70% of the concentration in blood.
Normal CSF glucose levels - 45–80 mg/dL
All of the following are TRUE about Cryptococcal neoformans EXCEPT -
AIDS-associated cryptococcosis account for 85% of all patients diagnosed with cryptococcosis
P carinii pneumonia (PCP) the recommended secondary prophylaxis is -
P carinii pneumonia (PCP), the recommended secondary prophylaxis is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Subdural Empyema is most commonly caused by -
Subdural Empyema most commonly involves -
About 95% of subdural empyemas are located within the cranium
Most subdural empyemas involve the frontal lobe
5% involve the spinal neuraxis.
Commonest cause of Subdural Empyema in cases secondary to cranial trauma -
Commonest cause of Subdural Empyema - cases secondary to cranial trauma or surgical procedures -
- Staphylococcus aureus
Nephrology MCQs- III
Creatinine clearance declines by an average of ---------- after age 40 years as part of the aging process.
Creatinine clearance declines by an average of 0.8 mL/min/yr after age 40 years as part of the aging process.
Creatinine is not a perfect indicator of GFR for the following reasons EXCEPT -
Creatinine is a product of muscle metabolism produced at a relatively constant rate and cleared by renal excretion. Which is good for being a perfect indicator of GFR.
All of the following are exogenous marker for GFR measurement EXCEPT -
Exogenous markers for GFR Measurement -
Inulin, Iohexol, Iothalamate
Endogenous markers for GFR Measurement - GFR is commonly estimated using serum levels of endogenous markers. Creatinine, urea, cystatin C, beta-trace protein, and beta-2 microglobulin.
Reduced BUN levels are seen in -
Reduced BUN levels are seen in liver disease and in the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH).
BUN : creatinine ratio increases in all of the following EXCEPT -
BUN : creatinine ratio -
low BUN-to-creatinine ratio may be caused by
-diet low in protein,
- severe muscle injury[rhabdomyolysis] ,
- pregnancy, cirrhosis,
- syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH).
All of the following are CORRECT EXCEPT -
Creatinine clearances - overestimate GFR
Urea clearances - underestimate GFR
All of the following are indications of Renal biopsy EXCEPT =
Uncontrollable severe hypertension - Contraindication for Renal Biopsy
AKI is defined as an absolute increase in serum creatinine by --------- within 48 hours
AKI is defined as an absolute increase in serum creatinine by 0.3 mg/dL or more within 48 hours or
a relative increase of at least 1.5 times baseline that is known or presumed to have occurred within 7 days.
RIFLE criteria is used for evaluation of -
RIFLE criteria, proposed by the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) group, aid in assessment of the severity of a person's acute kidney injury.
AKI can be diagnosed if any one of the following is present EXCEPT:
Introduced by the KDIGO in 2012 - specific criteria exist for the diagnosis of AKI.
AKI can be diagnosed if any one of the following is present:
Increase in SCr by ≥0.3 mg/dl (≥26.5 μmol/l) within 48 hours; or
Increase in SCr to ≥1.5 times baseline, which has occurred within the prior 7 days; or
Urine volume < 0.5 ml/kg/h for 6 hours.
Nephrology MCQs-II
Proteinuria in adults is defined as excessive protein excretion in the urine, generally greater than --------------
Proteinuria is defined as excessive protein excretion in the urine, generally greater than 150 mg/24 hours in adults
Which of the following cast is not indicative of kidney disease ?
Hyaline casts - Not indicative of kidney disease
Hyaline casts seen in cases -
- Concentrated urine,
- febrile disease,
- diuretic therapy,
- after strenuous exercise
Red cell casts - Glomerulonephritis
White cell casts - Indicative of infection or inflammation, Pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis,
Renal tubular cell casts -Acute tubular necrosis, interstitial nephritis
Granular (muddy brown) casts- Nonspecific; can indicate acute tubular necrosis
Bence Jones proteins are missed with dipstick analysis because -
Evaluation of proteinuria by urine dipstick does not actually measure protein but instead detects the negative electrochemical charge that characterizes albumin.
Bence Jones proteins - positively charged so Bence Jones proteins are missed with dipstick analysis.
Urine dipstick for proteins DIRECTLY detects -
Evaluation of proteinuria by urine dipstick does not actually measure protein but instead detects the negative electrochemical charge that characterizes albumin.
Urine protein to creatinine ratio (P/C ratio) is a fast and simple method of detecting -
Urine protein to creatinine ratio (P/C ratio) is an alternative, fast and simple method of detecting and estimating the quantitative assessment of proteinuria.
Bence Jones proteins can be detected by the addition of --------------- to the urine specimen
Bence Jones proteins can be detected by the addition of sulfosalicylic acid to the urine specimen
Creatinine clearance is approximately -------- mL/min in healthy young men
Creatinine clearance is approximately 100 mL/min in healthy young women and 120 mL/min in healthy young men
Cockcroft-Gault formula is used to measure -
Cockcroft-Gault formula: Estimated creatinine clearance rate (eCCR)
Creatinine clearance can be estimated using serum creatinine levels.
Cockcroft-Gault formula uses all of the following EXCEPT -
The resulting CrCl is multiplied by 0.85 if the patient is female to correct for the lower CrCl in females.
Which is the main predictor for Creatinine clearance in Cockcroft-Gault formula?
The Cockcroft-Gault formula is dependent on age as its main predictor for Creatinine clearance.
Nephrology MCQs-I
Urinalysis should be done within ------------------- after collection to avoid destruction of formed elements.
Urinalysis should be done within 1 hour after collection to avoid destruction of formed elements.
Precipitation of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein in the renal tubule and formation of urinary casts are likely to form when -
Tamm-Horsfall protein (THP) is exclusively produced by renal tubular cells of the -
Distal loop of Henle
All of the following are correct regarding Bence Jones protein EXCEPT -
Detection of Bence Jones protein may be suggestive of multiple myeloma or Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. More common are kappa chains (most of the time) than lambda
Tamm–Horsfall protein also known as -
myeloma protein - -M protein, M component, M spike, spike protein, or paraprotein.
Uromodulin (UMOD), also known as Tamm–Horsfall protein (THP), is a Zona pellucida-like domain-containing glycoprotein
Urinary Cast formation is pronounced in environments - 1. Low flow, 2. Concentrated salts, 3. Low pH
Cast formation is pronounced in environments favoring protein denaturation and precipitation (low flow, concentrated salts, low pH)
All of the following are TRUE about Hyaline casts EXCEPT -
Low urine flow, concentrated urine, or an acidic environment can contribute to the formation of hyaline casts
Findings of muddy brown casts in urine sediment are highly suggestive of -
Findings of granular, muddy brown casts in urine sediment are highly suggestive of tubular necrosis
Red blood cell casts seen in all EXCEPT-
Red blood cells within the cast is always pathological and is strongly indicative of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, or Goodpasture's syndrome.
White blood cell casts
Indicative of inflammation or infection, the presence of white blood cells within or upon casts strongly suggests pyelonephritis,
In Acute tubular necrosis the diagnosis is made by a FENa (fractional excretion of sodium)-
Acute tubular necrosis is classified as a "renal" (i.e. not pre-renal or post-renal) cause of acute kidney injury.
Diagnosis is made by a FENa (fractional excretion of sodium) > 3% and presence of muddy casts (a type of granular cast) in urinalysis.
Medicine Review MCQs-X
Which of the following is a Melanocyte derived Giant cell -
Starburst giant cells are multi-nucleated melanocytes with a stellate appearance due to its prominent dendritic processes. These are useful indicator for the diagnosis of lentigo maligna from photo-damaged skin
Lentigo maligna is a subtype of melanoma in situ that is characterized by an atypical proliferation of melanocytes within the basal epidermis; lentigo maligna that invades the dermis is termed lentigo maligna melanoma
Warthin–Finkeldey cell is a type of giant cell found in -
Warthin–Finkeldey giant cell found in
- Hyperplastic lymph nodes early in the course of measles
- HIV-infected individuals,
- Kimura disease,
- Rarely in neoplastic (e.g. lymphoma) and non-neoplastic lymph node disorders
Tzanck giant cells seen in all of the following EXCEPT -
Tzanck giant cells
Multi-nucleated giant cell with molding of the nuclei as they are crowded together.
These are epidermal cells that are much larger than the normal epidermal cells.
What is the order of Giant cells -
Langhans’ Giant Cells , Foreign body giant cells, Touton Giant Cell
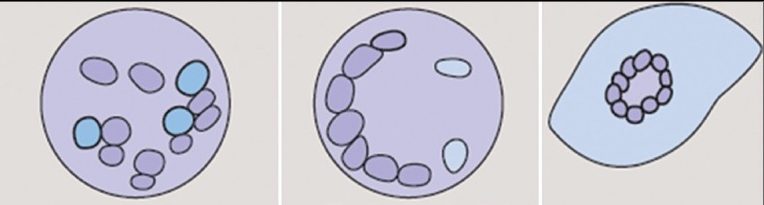 1, 2, 3
1, 2, 3
Which organism associated with rat-bite fever?
Spirillum minus is an organism associated with rat-bite fever .
It stains gram-negative and has a coiled rod shape.
“Henderson-Patterson’s bodies” seen in -
Henderson-Paterson bodies, can measure 35µm in diameter. Ultrastructural studies have shown that these bodies are membrane-bound sacs that contain numerous molluscum contagiosum virions
In which of the following Cytological Examination shows -Cigar-shaped spindle cells?
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Kaposi’s sarcoma is caused by a combination of immune suppression (such as due to HIV/AIDS) and infection by Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8 - also called KS-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)
Koilocyte is a type of squamous epithelial cell seen after viral infection with -
koilocyte is a squamous epithelial cell that has undergone a number of structural changes
koilocyte is found due to infection of the cell by human papillomavirus (HPV).
Leishman-Donovan bodies seen in cytological examination of -
L. donovani is the causative agent of visceral leishmaniasis, known as kala-azar ("black fever", particularly in India)
What is the causative organism of cat-scratch disease?
Spirillum minus - an organism associated with rat-bite fever
Bartonella henselae - causative organism in cat-scratch disease
Medicine Review MCQs-IX
Mycobacterium tuberculosis commonly infects -
Macrophages
Infected macrophages in the lung, through their production of chemokines, attract inactivated monocytes, lymphocytes, and neutrophils , none of which kill the bacteria very efficiently .
Granulomatous focal lesions composed of - macrophage-derived giant cells and lymphocytes begin to form.
Acid-fast microscopy may be reported based on the World Health Organization and International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases (WHO-IUTLD) :
For the Ziehl-Neelsen Method (via light/brightfield microscopy)
More than 10 AFB per field in at least 20 visual fields -
The results of acid-fast microscopy may be reported based on the World Health Organization and International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases (WHO-IUTLD):For the Ziehl-Neelsen Method (via light/brightfield microscopy)-
No Acid-fast bacilli (AFB) seen -
Report as "0". It means no AFB was observed in 2 lengths (i.e., 300 visual fields), thus, conferring a "negative" result.
1-9 AFB in 1 length - Record the actual number of AFB seen (e.g. +1, +2, +9). Note that the plus sign should precede the number. This is also referred to as a scanty positive result.
10-99 AFB in 1 length - Report as "1+". Note that the plus sign should come after the number. This is a positive result.
1-10 AFB per field in at least 50 visual fields - Report as "2+". Note that the plus sign should come after the number. This is a positive result.
More than 10 AFB per field in at least 20 visual fields - Report as "3+". Note that the plus sign should come after the number. This is a positive result and is highly infectious.
For Auramine Method (via fluorescence microscopy at 400x magnification) more than 60 AFB in 1 length - Report as
Microscopy of M. tuberculosis caseating granulomas revealed a type of cell that has a "horseshoe" pattern of nuclei. What is the name of that cell?
M. tuberculosis is characterized in tissue by caseating granulomas containing Langhans giant cells, which have a "horseshoe" pattern of nuclei.
Touton giant cells are seen in all of the following EXCEPT?
Touton giant cells are a type of multinucleated giant cell seen in lesions with high lipid content such as -
- fat necrosis,
- xanthoma,
- xanthelasma
- xanthogranulomas.
They are also found in dermatofibroma
What is the name of pointed Microscopic structure?
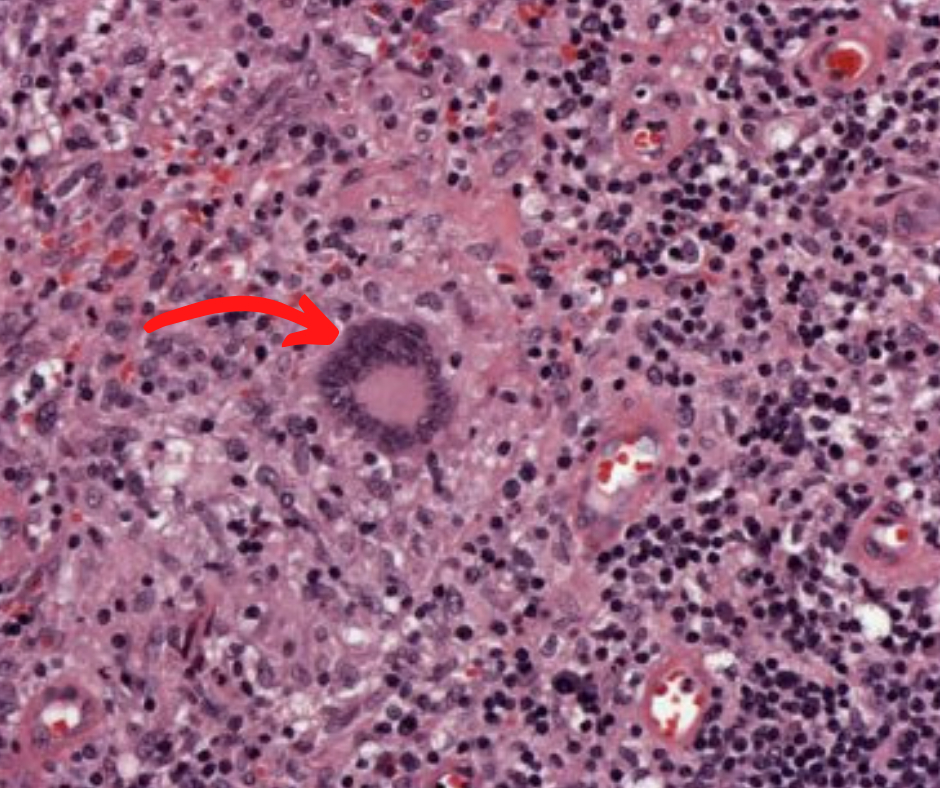
Diagnosis - Granulomatous lesion
Langhans giant cell
Autoantibodies against LRP4 have been seen in some cases of -
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune - T-cell-dependent disease.
Acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibodies are found in approximately 80% of patients,
Other antibodies
Muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (Musk) antibodies [Anti-MUSK]
Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 4 (LRP4),
Agrin antibodies ,
Rapsyn antibodies ,
Striational antibodies
All of the following are LESS COMMON autoantibodies in Myasthenia Gravis EXCEPT -
The most common antibodies detected in MG are antibodies against acetylcholine receptors (AChRs), muscle-specific kinase (MuSK) and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 (LRP4)
Additional antibodies of interest in MG are directed against agrin, titin, KV1.4, ryanodine receptors, collagen Q, and cortactin
Antibodies to cytolethal distending toxin B (CdtB) and vinculin are novel biomarkers that rule-in and differentiate irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) from other causes of diarrhea and healthy controls.
What % of patients with MG may present with prominent bulbar symptoms?
20% of patients in MG Shows Bulbar symptoms
All of the following auto-antibody seen in Graves' disease EXCEPT ?
Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase (anti-GAD) are reliable serological markers of Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Anti-GAD antibodies [high titre] are associated with the stiff-person syndrome (60% sensitivity),
Medicine Review MCQs-VIII
Most common cause of anemia is ---------
Most common cause of anemia is iron deficiency
Most common cause of iron deficiency in adults ------
Bleeding is the most common cause of iron deficiency in adults
Pagophagia is the compulsive consumption of ------------
Pagophagia is the compulsive consumption of ice or iced drinks
Pagophagia has been shown to be associated with iron-deficiency anemia and responsive to iron supplementation
Omophagia (omo - phagia): the act of eating raw meat.
Geophagia (geo - phagia): a term that refers to the eating of earth substances especially chalky or clay substances.
In healthy populations fingernails grow at about -----mm/day and toenails at about ----- mm/day
In healthy populations fingernails grow at about 0.1mm/day and toenails at about 0.05mm/day
Mees' lines appear after an episode of poisoning with -
1.Arsenic
2.Thallium
3.Selenium
Mees' lines appear after an episode of poisoning with arsenic thallium or other heavy metals or selenium
Prolonged use of -------------- can lead to blue-gray staining of skin, fingernails
Prolonged use of minocycline can lead to blue-gray staining of skin, fingernails, and scar tissue.
Muehrcke's lines - all of the following are TRUE EXCEPT-
Muehrcke's lines -
Pale transverse bands
Thumb is usually not involved - in contrast to Mees' lines
Not grooved - contrast to Beau's lines,
Half and half nails also called as -
Half and half nails ("Lindsay's nails")- proximal portion of the nail white and the distal half red, pink, or brown, with a sharp line of demarcation between the two halves
Half and Half nails were significantly common in -
Half and Half nails were significantly more common in hemodialysis patients,
leukonychia was significantly more common in renal transplant patients
Menkes disease - all of the following are CORRECT EXCEPT -
Hair appears strikingly peculiar: kinky, colorless or silvery, and brittle
Like all X-linked recessive conditions, Menkes disease is more common in males than in females.
Medicine Review MCQs-VII
Waddling gait also known as -
Myopathic gait also known as waddling gait is a form of gait abnormality.
The "waddling" is due to the weakness of the proximal muscles of the pelvic girdle
Waddling gait seen in all of the following EXCEPT -
Conditions associated with a myopathic gait -
pregnancy,
congenital hip dysplasia,
muscular dystrophies,
spinal muscular atrophy
Scissors gait seen in -
Knees and thighs hit or cross in a scissors-like pattern when walking
The steps are slow and small. This type of gait occurs often in patients with spastic cerebral palsy.
Steppage gait seen in -
“high stepping” type of gait in which the leg is lifted high, the foot drops, appearing floppy, and the toes points downward, scraping the ground, when walking.
HTT gene is located on the short arm (p) of chromosome ----------
Huntington's disease is a progressive brain disorder caused by a single defective gene on chromosome 4
Mutated HTT is the cause of Huntington's disease
Motor symptoms of Parkinsonism result from the death of cells in -
Parkinsonism - motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra
Wilson's disease gene (ATP7B) is on chromosome number ------
Wilson's disease - inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern
Wilson's disease gene (ATP7B) is on chromosome 13
Which disease is the most common from a group of hereditary diseases that cause copper overload in the liver?
Wilson's disease is the most common from a group of hereditary diseases that cause copper overload in the liver.
All can cause cirrhosis at a young age
Lactic acidosis is seen in deficiency of -
Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency - Lactic acidosis and Hyperammonaemia
Overexpression of superoxide dismutase-1[SOD1]has been linked to the neural disorders seen in -
SOD1 is located in the cytoplasm, SOD2 in the mitochondria, and SOD3 is extracellular.
Overexpression of SOD1 has been linked to the neural disorders seen in Down syndrome
Medicine Review MCQs-VI
Erythropoietin belongs to which of the following?
Glycoprotein hormone
Which is the major extra-renal site of Erythropoietin production?
Liver
Liver production predominates in the fetal and perinatal period
Renal production predominates in adulthood.
All of the following are CORRECT about Erythropoietin EXCEPT:
Half-life in blood around 5 h
We should consider administration of Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents when the Hb level becomes ---------- g/dl in dialysis patients.
We should consider administration of Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents when the Hb level becomes <10 g/dl in dialysis patients.
For patients on dialysis, ESAs should be initiated for an Hb <10 g/dL and the dose should be reduced or interrupted when the Hb level approaches or exceeds 11 g/dL
Most dialysis patients who are treated with ESAs, advised to maintain Hb levels between -------------
Pooled analysis of nine randomized control trials on patients with chronic kidney disease indicates that patients have higher mortality and morbidity from cardiovascular-related events when the hemoglobin falls below 10 g/dL.
There was no benefit in survival in patients treated with Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents when the hemoglobin exceeded 13 g/dL,
Target hemoglobin levels and optimal levels generally fall between 11 and 12 g/dL with the knowledge that higher doses of ESAs may increase the risk for thrombotic events.
In most dialysis patients who are treated with ESAs, we maintain Hb levels between 10 and 11.5 g/dL. We do not target an Hb concentration >13 g/dL. Our practice is consistent with the KDIGO 2012 guidelines
Anemia is defined by WHO as a hemoglobin (Hb) concentration ---------- for premenopausal females
Anemia is defined by WHO as a hemoglobin (Hb) concentration <13 g/dL for adult males and postmenopausal females and an Hb concentration <12 g/dL for premenopausal females
Longest half life of ESA -
Darbepoetin-α and methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin β (Continuous Erythropoietin Receptor Activator; CERA) were registered in 2010 and 2011 respectively, all for use during the predialytic phase of CKD.
Epoetin-α and -β are short-acting ESAs, and darbepoetin-α and CERA are long-acting ESAs.
Hemoglobin A- represents approximately ---------- of circulating hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin A- represents approximately 98% of circulating hemoglobin.
Reticulocyte hemoglobin concentration of less than ---------- support iron deficiency in the setting of inflammation
The challenge is the diagnosis of iron deficiency in the setting of the anemia of inflammation
Tests support iron deficiency in the setting of inflammation: a reticulocyte hemoglobin concentration of less than 28 pg
Which of the following is used as an iron replacement to prevent anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease who are on dialysis?
Ferric pyrophosphate citrate is used as an iron replacement to prevent anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease who are on dialysis.
Medicine Review MCQs-V
Oppositional paratonia also called as -
Oppositional paratonia - "gegenhalten" occurs when subjects involuntarily resist to passive movements, Facilitatory paratonia - "mitgehen" occurs when subjects involuntary assist passive movements.
Paratonia have been associated with cognitive impairment, particularly in relation to -
Paratonia have been associated with cognitive impairment or mental disorders, particularly in relation to frontal lobe dysfunction.
All of the following are seen in parkinsonism EXCEPT -
Coarse, slow tremor seen in Parkinsonism
All of the following are correct regarding tremor of Parkinsonism EXCEPT -
Disappears during voluntary movement
Typically appears in only one hand
It typically appears in only one hand, eventually affecting both hands as the disease progresses
Frequency of PD tremor is between 4 and 6 hertz
Reduced motivation or ability to experience pleasure is called -
Anhedonia is a diverse array of deficits in hedonic function, including reduced motivation or ability to experience pleasure
Alexithymia – a condition describing people who "lack words for their feelings
Avolition, as a symptom of various forms of psychopathology, is the decrease in the ability to initiate and persist in self-directed purposeful activities
The treatment of choice for Hashimoto thyroiditis -
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis -Treatment of choice for Hashimoto thyroiditis (or hypothyroidism from any cause) is thyroid hormone replacement.
The drug of choice is orally administered levothyroxine sodium.
Which is correct for Subclinical hypothyroidism?
Subclinical hypothyroidism suggests mild thyroid failure,
Evidenced by an elevated TSH above 4.0 μ IU/mL and normal free T4 levels
Hashimoto Thyroiditis rate of progression to overt hypothyroidism is estimated to be about ----- % per year.
The rate of progression to overt hypothyroidism is estimated to be about 5% per year.
Best marker of progression of Hashimoto Thyroiditis to overt hypothyroidism is -
Best marker of progression of Hashimoto Thyroiditis to overt hypothyroidism is a combination of an elevated TSH level with the presence of thyroid autoantibodies, namely anti-TPO and anti-Tg antibodies.
Hashimoto's disease affects more -------- sex and ---------- age group.
Hashimoto's disease affects more women than men.
Most often appears between ages 40 and 60.
Medicine Review MCQs-IV
Most common demyelinating disease -
Multiple sclerosis [encephalomyelitis disseminata] is the most common demyelinating disease.
Neuromyelitis optica - Devic's disease
In patients of porphyria predisposed to neurovisceral attacks all of the following can be a part of management EXCEPT-
Intravenous glucose,-terminate acute attacks through a reduction in δ-aminolaevulinic acid (ALA) synthetase activity, leading to reduced ALA and porphyrin synthesis.
Administration of haem (haematin or haem arginate) has been shown to reduce metabolite excretory rates, relieve pain and accelerate recovery.
Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogues - suppression of the menstrual cycle.
Exogenous oestrogens -Oral contraceptive pill is a common precipitating factor
Pseudohypoglycemia is an event during which the person with diabetes reports typical symptoms of hypoglycemia but has a measured glucose level
Pseudohypoglycemia is an event during which the person with diabetes reports typical symptoms of hypoglycemia but has a measured glucose level >70 mg/dL
Which is the first Physiologic response to hypoglycemia in normal subjects?
First defense- decrease in insulin secretion
glycemic threshold of 80 to 85 mg/dL
Second defense - increase in glucagon secretion
glycemic threshold for glucagon is 65 to 70 mg
Third defense - increase in epinephrine secretion
glycemic threshold for epinephrine secretion is also 65 to 70 mg/dL
Which is the first Physiologic response to hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes and longstanding type 2 diabetes. ?
First defense- to suppress insulin release, cannot occur in patients with absolute beta cell failure, ie, those with type 1 diabetes and longstanding type 2 diabetes.
Main defense against hypoglycemia is increased release of counter-regulatory hormones- glucagon and epinephrine, which raise plasma glucose concentrations by stimulating glucose production and by antagonizing the insulin-induced increase in glucose utilization.
Hypoglycemia causes neuronal death when glucose levels have fallen below ------- for some period.
Hypoglycemia causes neuronal death when glucose levels have fallen below 18 mg/dL for some period.
Impairment of action and judgment usually becomes obvious below -------- mg/dl
Impairment of action and judgment usually becomes obvious below 2.2 mmol/l (40 mg/dl).
As blood glucose levels fall below 0.55 mmol/l (10 mg/dl), most neurons become electrically silent and nonfunctional, resulting in coma.
Neuroglycopenia without hypoglycemia is called -
Hypoglycorrhachia is defined as an abnormally low glucose concentration within the cerebrospinal fluid is often suggestive of an underlying infectious or systemic process.
This is often defined as a glucose concentration less than 40 mg/dL.
Hypoglycorrhachia - Severe neuroglycopenic effects occurred despite normal blood glucose levels.
Symptomatic hypoglycemia occurring within four hours after a high carbohydrate meal is
Reactive hypoglycemia- is a term describing recurrent episodes of symptomatic hypoglycemia occurring within four hours after a high carbohydrate meal in people with and without diabetes.
In the US, hypoglycemia is when the blood glucose level is below ----- mg/dl within the first 24 hours of life and below ------ mg/dl thereafter
In the US, hypoglycemia is when the blood glucose level is below 30 mg/dl within the first 24 hours of life and below 45 mg/dl thereafter