Contents
- 1 What is the Incubation period of Staphylococcus aureus Food Poisoning ?
- 2 5th June is known as -
- 3 Salter’s scale used in which of the following condition?
- 4 Rule of Halves is seen in
- 5 Waist Hip Ratio indicates Obesity in Women when
- 6 Which hepatitis virus carries highest risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma as a complication?
- 7 Most common type of glomerulonephritis described in association with hepatitis B -
- 8 What is the strongest risk factor associated with an increased HCC risk in HBV infection?
- 9 Anemia caused by a disorder of the porphyrin pathway leading to ineffective erythropoiesis is called -
- 10 What is the type of cell in the image?
- 11 What is the cell shown in Image?
- 12 What are Echinocytes?
- 13 All of the following Causes Aquired sideroblastic anemis EXCEPT :
- 14 Which of the following can be a diagnosis in case of mostly showing small and medium-sized arteries vasculitis sparing pulmonary atreries ?
- 15 Most common site of rash in SLE -
What is the Incubation period of Staphylococcus aureus Food Poisoning ?
The incubation period for S. aureus food poisoning is between 2 and 4 hours (range 30 minutes to 8 hours)
5th June is known as -
UN designates 5 June as World Environment Day in 1972; two years later, the day is celebrated for the first time under the slogan “Only One Earth.”
1st December - World AIDS Day
1st July - Doctors Day
31st May No Tobacco Day
Salter’s scale used in which of the following condition?
SALTER SCALE -Spring hanging scale -
Used for taking weight of children under 9 years.
Weigh up to 25 kg
Graduated by 0.1kg (100g) increments.
Rule of Halves is seen in
rule of halves' for hypertension suggests -
-Half the population with hypertension are not known,
-Half of those known are not treated
-Half of those treated are not controlled.
Waist Hip Ratio indicates Obesity in Women when
Obesity is diagnosed when Waist Hip Ratio -
Women - >0.85,
Men > 1.00
WHR has been found to be a more efficient predictor of mortality in older people (>75 years of age) than waist circumference or BMI.
Evidence suggests that WHR is an accurate somatic indicator of reproductive endocrinological status and long-term health risk.
Which hepatitis virus carries highest risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma as a complication?
Hepatitis B viral load is the strongest risk factor associated with an increased HCC risk, independent of HBeAg status and cirrhosis. Chronic inflammation caused by long-term exposure to high levels of HBV DNA will increase the risk of subsequent HCC.
Most common type of glomerulonephritis described in association with hepatitis B -
Three most common types of kidney disease resulting from HBV infection are:
●Membranous nephropathy
●Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN)
●Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)
most common type of glomerulonephritis described in association with hepatitis B is membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN), found mainly in children. However, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) and, even more rarely, immunoglobulin (Ig) A nephropathy, have also been identified.
What is the strongest risk factor associated with an increased HCC risk in HBV infection?
Hepatitis B viral load is the strongest risk factor associated with an increased HCC risk, independent of HBeAg status and cirrhosis. Chronic inflammation caused by long-term exposure to high levels of HBV DNA will increase the risk of subsequent HCC.
Anemia caused by a disorder of the porphyrin pathway leading to ineffective erythropoiesis is called -
In Sideroblastic anemias - affected erythroblasts, abnormal, iron-laden mitochondria appear to encircle the nucleus, giving rise to the defining morphological feature of sideroblastic anemias, the RING SIDEROBLAST
What is the type of cell in the image?
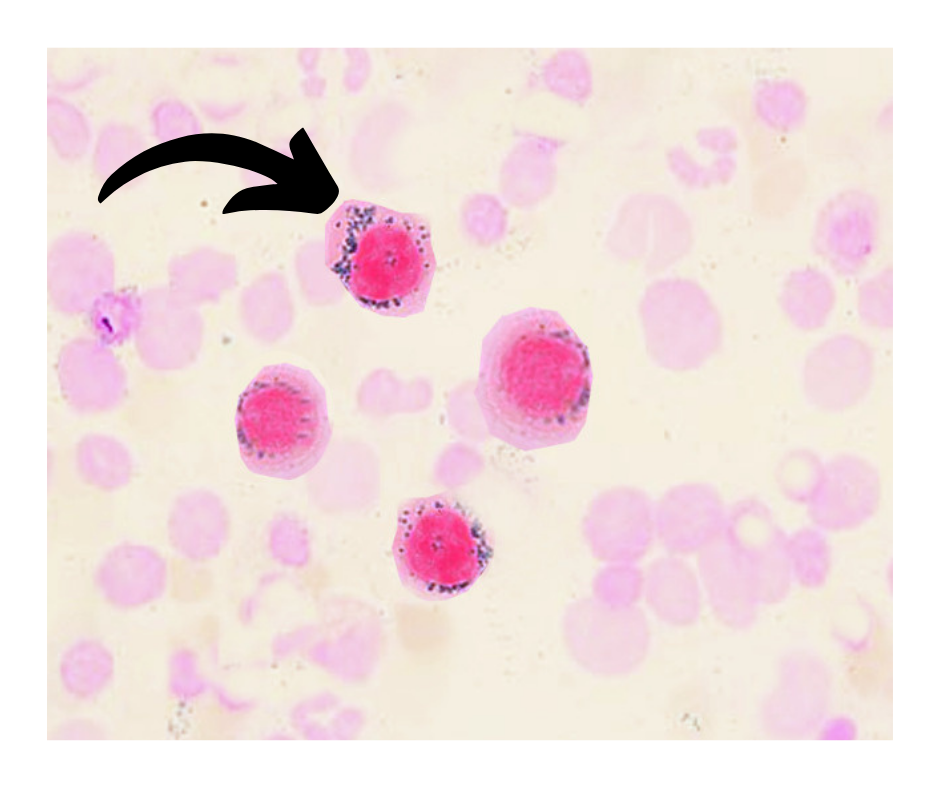

RING SIDEROBLAST
Feature of sideroblastic anemias, the RING SIDEROBLAST
What is the cell shown in Image?
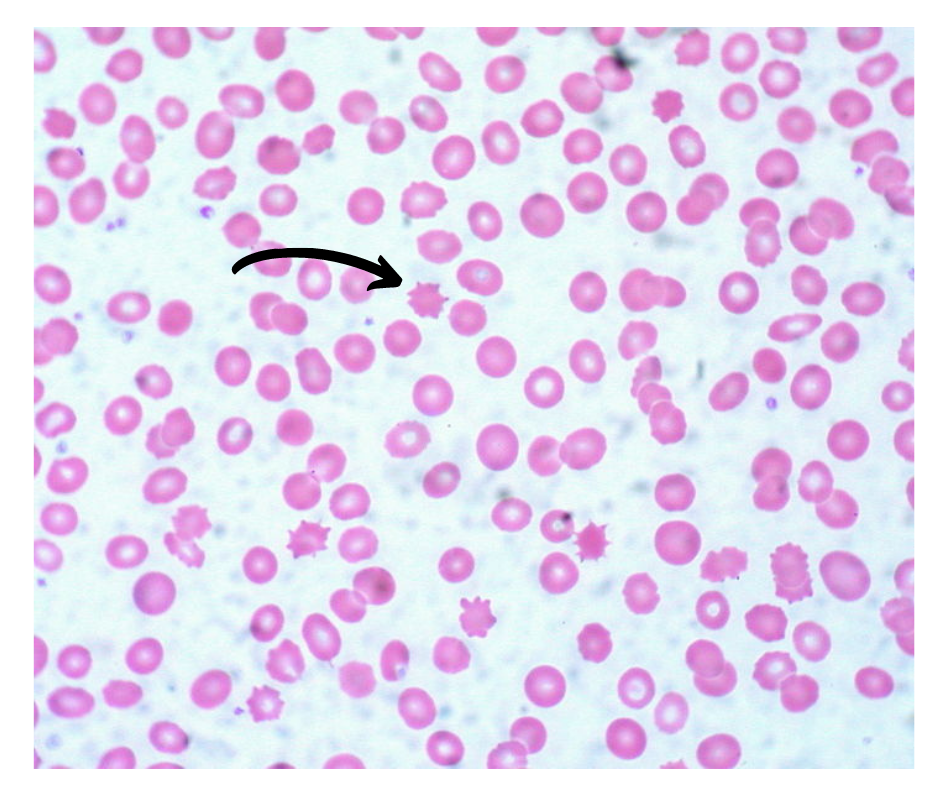

Spur cells, or acanthocytes (from the Greek word acantha, "thorn"), are erythrocytes covered with spikelike projections.
They are characterized by diminished deformability, which is responsible for their entrapment and destruction in the spleen.
Acanthocytosis [spur cells] is associated with advanced liver disease, regardless of the primary cause
Alectinib, an anaplastic lymphokinase (ALK) inhibitor used for the treatment of non–small cell lung cancer, has been associated with spheroacanthocytosis without causing significant hemolytic anemia.
What are Echinocytes?
Echinocytes can be distinguished from acanthocytes by the shape of the projections, which are smaller and more numerous than in acanthocytes[Spur Cells] and are evenly spaced.
Echinocytes also exhibit central pallor.
Seen in conditions:
artifact of staining or drying, echinocytes are associated with:[5]
Uremia and chronic kidney disease
Liver disease
pyruvate kinase deficiency
hypophosphatemia
hyperlipidemia
Phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency
Disseminated malignancy
Myeloproliferative disorders
All of the following Causes Aquired sideroblastic anemis EXCEPT :
Acquired sideroblastic anemias-
Copper deficiency, which can occur as a part of -
Malabsorption,
Nephrotic syndrome - loss of ceruloplasmin
Gastric surgery - Decreased Copper Absorption
Which of the following can be a diagnosis in case of mostly showing small and medium-sized arteries vasculitis sparing pulmonary atreries ?
Polyarteritis nodosa - Small and Medium sized vessel vasculitis
Takayasu arteritis- Large vessels including aorta and arch branches,
Giant cell arteritis - Superficial temporal artery, other medium- and large-sized vessels Example - those supplying the head, eyes and optic nerves
Most common site of rash in SLE -
Red rash which is most commonly on the face

