Mechanism of Positive Hoffmann’s Reflex
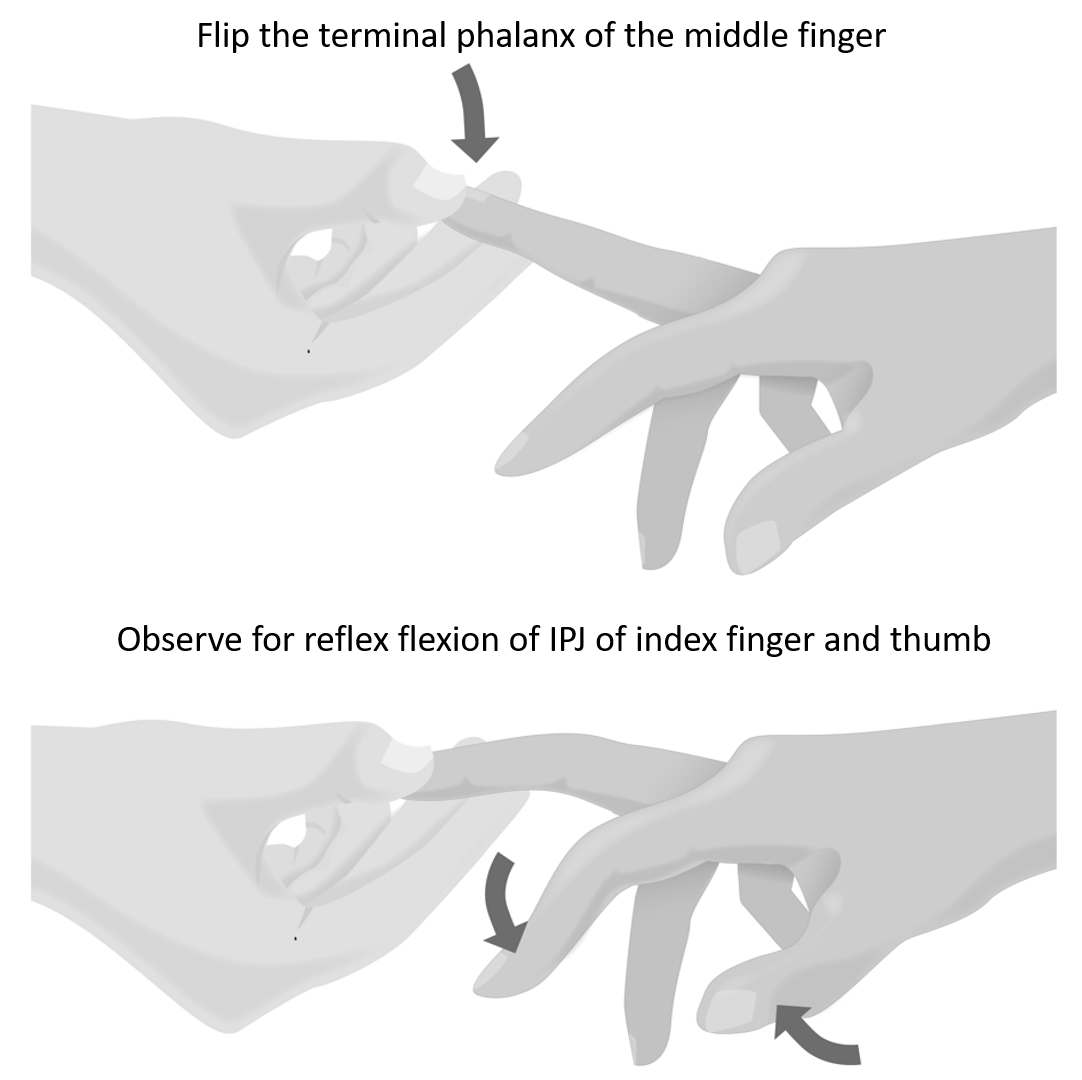
Mechanism of Positive Hoffmann’s Reflex.
Upper motor neuron lesions cause an increase in gamma motor neuron activity and a decrease in inhibitory interneuron activity, resulting in a state of hyperexcitability of alpha motor neurons
Hyperreflexia in the setting of upper motor neuron dysfunction
Sudden stretch of the finger flexors causes involuntary finger flexor contraction due to activation of a monosynaptic stretch reflex.
Exaggeration of the reflex is caused by hyperreflexia in the setting of upper motor neuron dysfunction.
Upper motor neuron lesions cause an increase in gamma motor neuron activity and a decrease in inhibitory interneuron activity, resulting in a state of hyperexcitability of alpha motor neurons