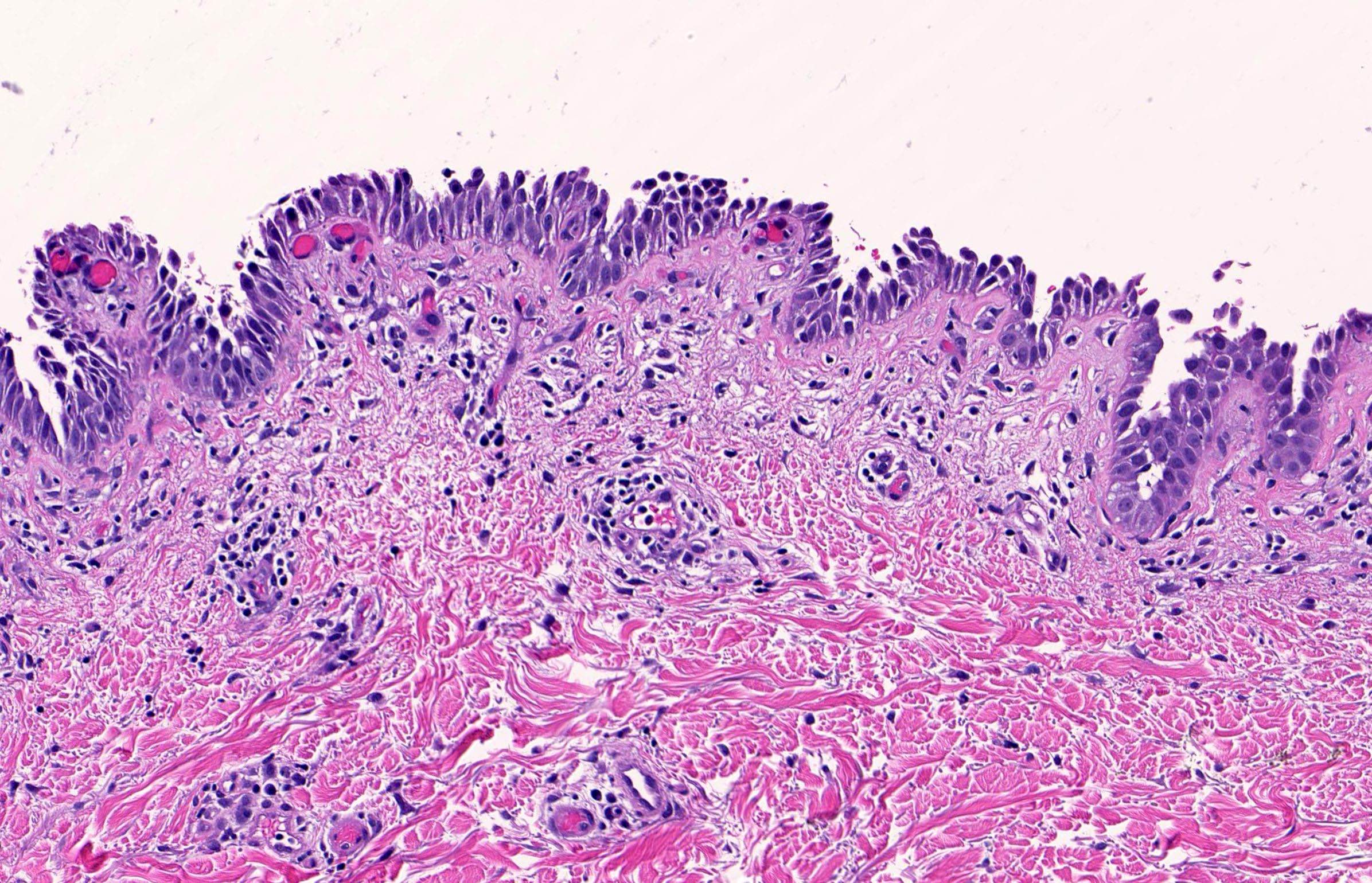
Tomb Stone Appearance
Contents
- 1 Tomb Stone Appearance is Classically described in the histopathology of
- 2 Tombstone sign – Pemphigus vulgaris:
- 3 Most common form of pemphigus
- 4 Most common form of pemphigus
- 5 Pemphigus vulgaris most commonly presents with
- 6 Pemphigus vulgaris is classified as
- 7 In Pemphigus vulgaris antibodies are formed against
- 8 Which Mutations are the main cause of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
- 9 Which sign is positive in Pemphigus vulgaris
- 10 Which is the is the dominant autoantibody subclass in PV and correlates with disease activity
- 11 Which is the is the dominant autoantibody subclass in PV and correlates with disease activity
- 12 Row of the tomb stone
- 13 Pathophysiology
- 14 Pathophysiology
- 15 Pemphigus vulgaris Pathophysiology
- 16 Pathophysiology
- 17 IgA pemphigus Pathophysiology
Tomb Stone Appearance is Classically described in the histopathology of
A. Bullous pemphigoid
B. Pemphigus vulgaris
C. Rhinophyma
D. Dermatitis herpetiformis
Tombstone sign – Pemphigus vulgaris:
- Suprabasal acantholysis
- Basal layer remains attached (tombstone sign)
Most common form of pemphigus
A. Pemphigus vulgaris
B. IgA pemphigus
C. Pemphigus foliaceus
D. Paraneoplastic pemphigus
Most common form of pemphigus
A. Pemphigus vulgaris
B. IgA pemphigus
C. Pemphigus foliaceus
D. Paraneoplastic pemphigus
Pemphigus vulgaris most commonly presents with
A. Anus
B. Cutaneous blisters
C. Conjunctiva
D. Oral blisters
Pemphigus vulgaris is classified as
A. Type I hypersensitivity reaction
B. Type II hypersensitivity reaction
C. Type III hypersensitivity reaction
D. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction
In Pemphigus vulgaris antibodies are formed against
A. Connexins
B. Desmosomes
C. Gap Junctions
D. Actin filaments
Which Mutations are the main cause of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
A. Connexins
B. Desmosomes
C. Gap Junctions
D. Actin filaments
Which sign is positive in Pemphigus vulgaris
A. Abadie’s sign
B. Nikolsky sign
C. Bancroft’s sign
D. Battle’s sign
Which is the is the dominant autoantibody subclass in PV and correlates with disease activity
A. IgA
B. IgM
C. IgE
D. IgG
Which is the is the dominant autoantibody subclass in PV and correlates with disease activity
A. IgG1
B. IgG2
C. IgG3
D. IgG4
Row of the tomb stone
Classically described in the histopathology of fresh blister of pemphigus vulgaris or drug-induced pemphigus.
Suprabasal splitting of the epidermis leads to blister formation,
With the basal layer still remaining adherent to the basement membrane – This gives the resemblance to the ‘Row of the tomb stone’.
Pathophysiology
Classified as a type II hypersensitivity reaction in which antibodies are formed against desmosomes
Pathophysiology
IgG or IgA autoantibody against epidermal antigens
Pemphigus vulgaris Pathophysiology
Pemphigus vulgaris: IgG to desmoglein 1 (skin) or desmoglein 3 (mucosa)
Pathophysiology
Pemphigus foliaceus – Pemphigus foliaceus: IgG to desmoglein 1
Paraneoplastic pemphigus: IgG to desmoplakin I, desmoplakin II, plectin, periplakin, envoplakin, BP230 or A2ML1
IgA pemphigus Pathophysiology
IgA to desmocollin 1- subcorneal pustular dermatosis [SPD] variant)
IgA to desmoglein 1, desmoglein 3 – intraepidermal neutrophilic [IEN] variant