Image Question-51
Contents
- 1 What is the cell marked in the image?
- 2 What is the cell marked in the image?
- 3 von Hansemann cells contains inclusions called
- 4 All are correct for Michaelis–Gutmann bodies Except
- 5 M-G bodies are a pathognomonic feature of
- 6 Malakoplakia is a condition associated with
- 7 Malakoplakia is seen most commonly in
- 8 Most common site of Malakoplakia in G.I Tract
- 9 Share the Infographic
What is the cell marked in the image?

What is the cell marked in the image?
A. Langhans giant cell
B. Touton giant cells
C. von Hansemann cells
D. Reed–Sternberg cell
von Hansemann cells contains inclusions called
A. Collins bodies
B. Michaelis–Gutmann bodies
C. Bunina bodies
D. Pappenheimer bodies
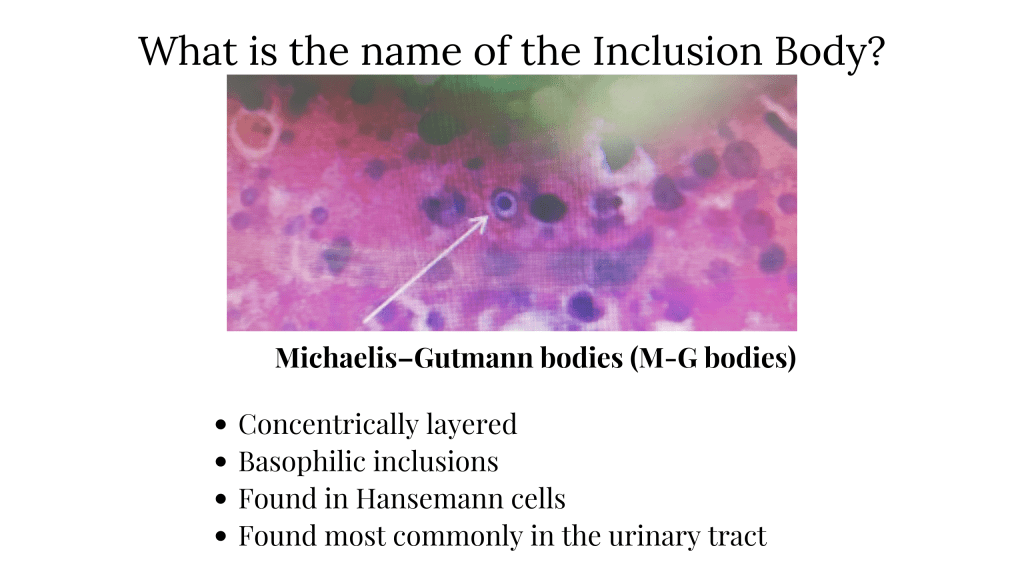
All are correct for Michaelis–Gutmann bodies Except
A. Concentrically layered
B. Basophilic inclusions
C. Found in Hansemann cells
D. Found in Spleen
M-G bodies are a pathognomonic feature of
A. Urothelial carcinoma
B. Malakoplakia
C. Renal cell carcinoma
D. Ureterocele
Malakoplakia is a condition associated with
A. Urothelial carcinoma
B. Chronic cystitis
C. Renal cell carcinoma
D. Ureterocele
Malakoplakia is seen most commonly in
A. Kidney
B. Ureter
C. Bladder
D. Urethra
Most common site of Malakoplakia in G.I Tract
A. Stomach
B. Duodenum
C. Colon
D. Ileum
Most common site of Malakoplakia – GU tract, particularly bladder
Most common site of Malakoplakia in Gastrointestinal tract – colon, followed by stomach and duodenum





