Image Question-20
Contents
- 1 What is the diagnosis?
- 2 Hairy cell leukemia usually classified as a subtype of
- 3 Hairy cell leukemia is accumulation of abnormal –
- 4 Which is the most common physical finding in hairy cell leukemia?
- 5 Commonest sites of involvement in hairy cell leukemia?
- 6 In-Shorts
- 7 Interleukin-2 receptor –
- 8 Classification of hairy cell leukemia
- 9 Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) stain-
What is the diagnosis?
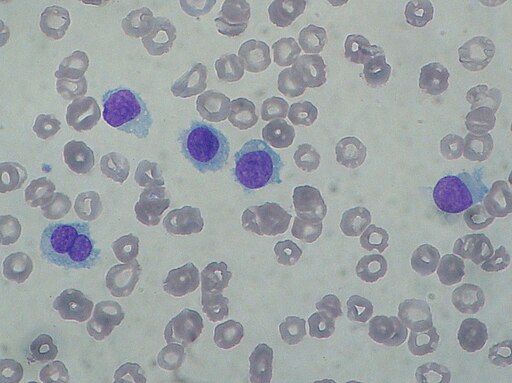
This picture is a contribution of Paulo Henrique Orlandi Mourao (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en).
B. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
C. Hairy cell leukemia
D. Chronic myeloid leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia usually classified as a subtype of
A. Acute myeloid leukemia
B. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
C. Acute lymphocytic leukemia
D. Chronic myeloid leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia is accumulation of abnormal –
A. Cytotoxic T Cells
B. Helper T Cells
C. Memory T Cells
D. B lymphocytes
Which is the most common physical finding in hairy cell leukemia?
A. Hepatomegaly
B. Lymphadenopathy
C. Splenomegaly
D. Pedal edema
Commonest sites of involvement in hairy cell leukemia?
A. liver
B. lymph node
C. skin
D. bone marrow
In-Shorts
Interleukin-2 receptor –
Hairy cells express and secrete an immune system protein called interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R).
The level increases as hairy cells proliferate, and decreases when they are killed.
Classification of hairy cell leukemia
- Hairy cell leukemia-classic
- Hairy cell leukemia-variant
- Hairy cell leukemia-Japanese variant
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) stain-
Tartrate does not inactivate the enzyme acid phosphatase within the neoplastic cells in hairy cell leukemia – because they are tartrate-resistant.
This is a feature not seen in most other leukemias and lymphomas. This is seen in hairy cell leukemia.
With tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) stain, the hairy cells show red granular cytoplasmic staining.
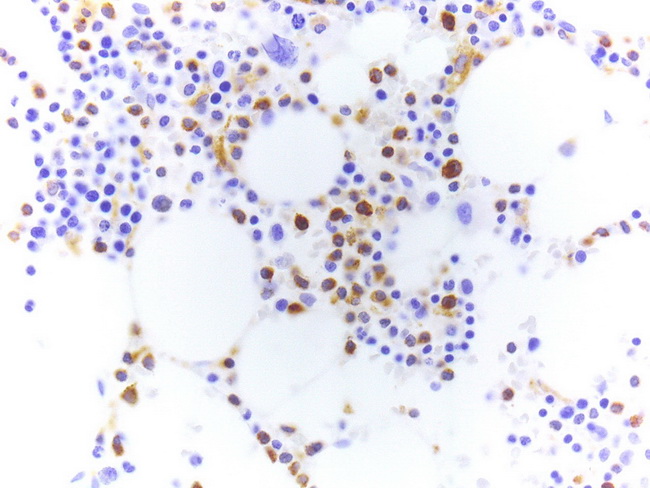
Nowadays, the TRAP cytochemistry has been largely replaced by TRAP immunohistochemistry (shown here). It must be remembered that TRAP immunostains are not as specific as TRAP cytochemistry and may stain other B-cell neoplasms.





