Image Question-14
Contents
- 1 What is the Diagnosis of the IMAGE?
- 2 Dawson’s fingers attributed to –
- 3 What is the pathological basis of Dawson fingers?
- 4 Pathology Flash Cards-1
- 5 Myocardial bridging- coronary artery anomaly
- 6 Hospital-acquired AKI
- 7 Expression of the Na, K-ATPase
- 8 Mitral Valve Anatomy
- 9 Peyer’s patches
- 10 Pancreatic Cancer – Review
- 11 Gallavardin phenomenon
- 12 Review Points
- 13 Image Question-43
- 14 Hobnail cells
- 15 Which of the following is used in treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension?
- 16 ‘Striped’ appearance
- 17 Steroidal Contraceptives
- 18 Clues to the diagnosis of Right ventricular hypertrophy
- 19 Epidermis : Basic Structure and Function
- 20 Commonest cause of mitral stenosis
- 21 Hürthle Cells
What is the Diagnosis of the IMAGE?
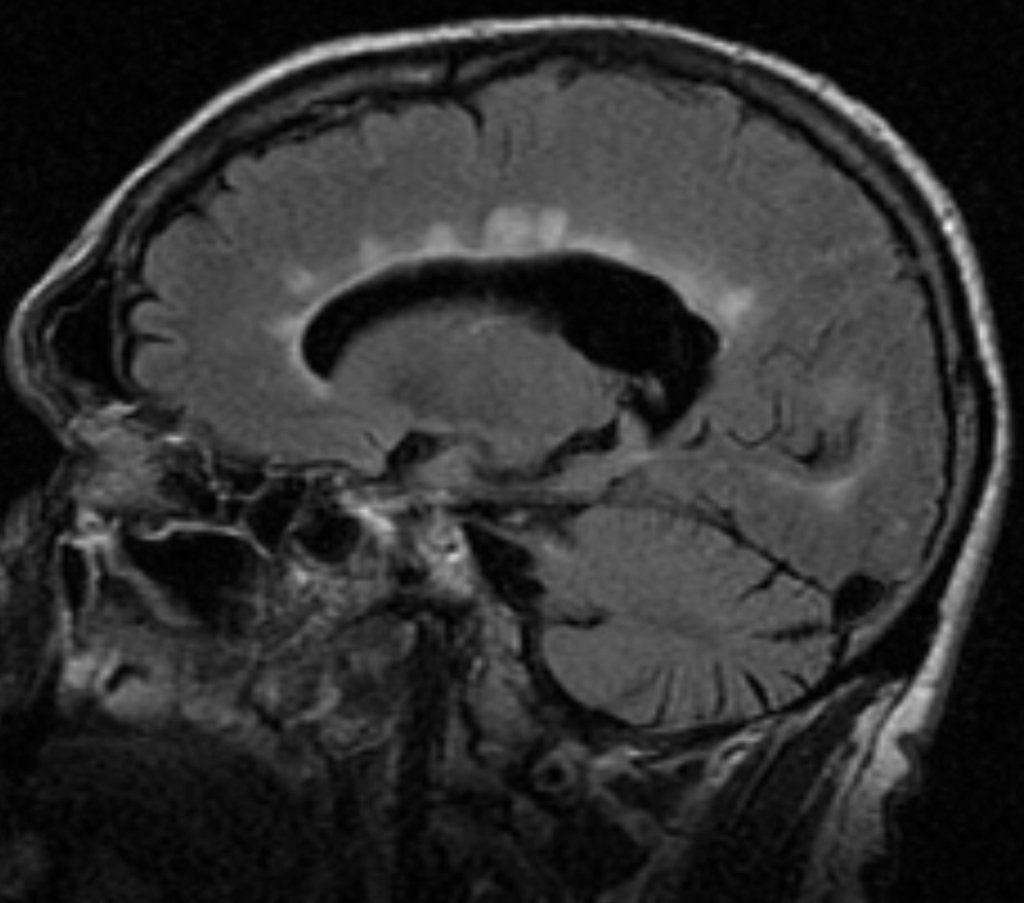
A. Salt and pepper sign
B. Dawson fingers
C. Dot-Dash sign
D. Empty delta sign
Dawson’s fingers attributed to –
A. Perilymphatic inflammation
B. Periarterial inflammation
C. Perineuronal inflammation
D.Perivenular inflammation
What is the pathological basis of Dawson fingers?
Dawson fingers – result of inflammation or mechanical damage by blood pressure around long axis of medullary veins.




