Image Question-14
Contents
- 1 What is the Diagnosis of the IMAGE?
- 2 Dawson’s fingers attributed to –
- 3 What is the pathological basis of Dawson fingers?
- 4 Medicine MCQs-25
- 5 Physiology Review -I
- 6 Wolf–Parkinson–White Syndrome
- 7 Ghost cells
- 8 What is the nature of the ‘second heart sound’ in Mitral Stenosis?
- 9 Bunina bodies
- 10 Murmur of Mitral Stenosis
- 11 Clinical Question-7
- 12 “Spike and dome” pulse
- 13 Ferruginous body
- 14 ECG Question-1
- 15 Megaloblastic Anemia MCQs
- 16 Cysticercosis
- 17 Gerbode defect
- 18 Anatomy MCQs-4
- 19 Oncology MCQs-1
- 20 Hirano bodies
- 21 Gynecology MCQs-I
What is the Diagnosis of the IMAGE?
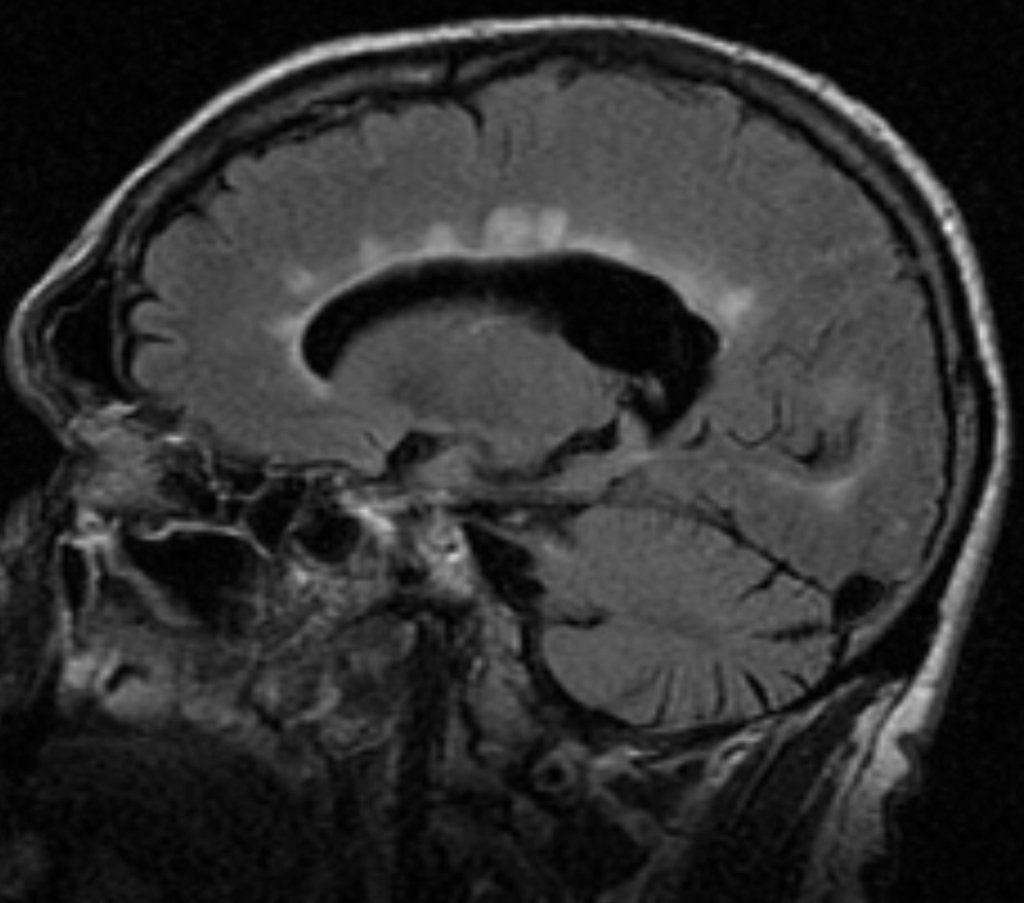
A. Salt and pepper sign
B. Dawson fingers
C. Dot-Dash sign
D. Empty delta sign
Dawson’s fingers attributed to –
A. Perilymphatic inflammation
B. Periarterial inflammation
C. Perineuronal inflammation
D.Perivenular inflammation
What is the pathological basis of Dawson fingers?
Dawson fingers – result of inflammation or mechanical damage by blood pressure around long axis of medullary veins.




