Frog sign
Contents
- 1 “Frog sign” is considered to be particularly helpful in making the diagnosis of typical
- 2 Frog sign
- 3 Frog sign
- 4 What is the mechanism of Frog Sign?
- 5 What is the diagnosis from ECG?
- 6 What is the difference between AVRT and AVNRT ?
- 7 What is the most common Type of AVNRT?
- 8 What are the Types of AVNRT?
- 9 Three primary types of atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) –
- 10 What is the basis of above classification of AVNRT ?
- 11 How can we classify AVNRT using RP interval?
“Frog sign” is considered to be particularly helpful in making the diagnosis of typical
[A] Ventriculat Tachycardia
[B] Atrial Flutter
[C] AVNRT
[D] Atrial Fibrillation
Frog sign
Frog sign
- The characteristic flapping or bulging appearance of the neck veins is also described as the “Frog sign.”
- “Frog sign” during narrow QRS complex tachycardia has been considered to be particularly helpful in making the diagnosis of typical AVNRT.
What is the mechanism of Frog Sign?
Parallel electrical activation of the atria and ventricles.
- Canon A waves which occur with AV dissociation result from simultaneous contractions of the atria and ventricles against closed mitral and tricuspid valves, causing reflux of blood into the neck veins.
The characteristic flapping or bulging appearance of the neck veins is also described as the “Frog sign.” - “Frog sign” during narrow QRS complex tachycardia has been considered to be particularly helpful in making the diagnosis of typical AVNRT.
What is the diagnosis from ECG?
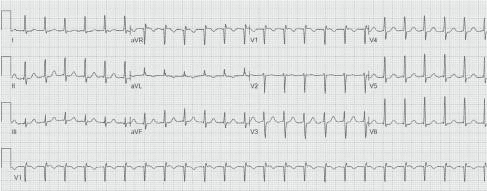
[A] Atrial flutter
[B] Atrial Fibrillation
[C] Idioventricular rhythm
[D] PSVT
What is the difference between AVRT and AVNRT ?
Atria and ventricles activate one after another “in sequence” with AVRT as opposed to “in-parallel” as during AVNRT
Since the atria and ventricles activate one after another “in sequence” with AVRT as opposed to “in-parallel” as during AVNRT, the interval between the QRS and the P waves is longer in the former, and retrograde P waves are often visible superimposed on the ST-T wave.
- Typical AVNRT – retrograde P waves occur early, so we either don’t see them (buried in QRS) or partially see them (pseudo R’ wave at terminal portion of QRS complex)
- AVRT – retrograde P waves occur later, with a long RP interval > 70 msec.

What is the most common Type of AVNRT?
[A] Slow-fast AVNRT
[B] Fast-fast AVNRT
[C] Fast-slow AVNRT
[D] Slow-slow AVNRT
What are the Types of AVNRT?
| SVT – AVNRT | CLASSIFICATION | ||
| 1 | Slow-fast AVNRT | Typical AVNRT | Most common type of AVNRT |
| 2 | Fast-slow AVNRT | Uncommon type of AVNRT | |
| 3 | Slow-slow AVNRT | Atypical type of AVNRT |
Three primary types of atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) –
- Slow-fast AVNRT: – typical AVNRT, this is the most common type of AVNRT.
- Fast-slow AVNRT: – uncommon type of AVNRT.
- Slow-slow AVNRT: – atypical type of AVNRT
What is the basis of above classification of AVNRT ?
- These types are classified based on the ratio of atrial-His/His-atrial intervals, the VA interval, and the site of earliest retrograde atrial activation.
How can we classify AVNRT using RP interval?
- The RP interval – the time between the R-wave and P-wave
RP interval – can also be used to differentiate between the types of AVNRT. - Typical AVNRT – Short RP interval
- Atypical and very atypical AVNRT – long RP interval.





