ECG Question-2
Contents
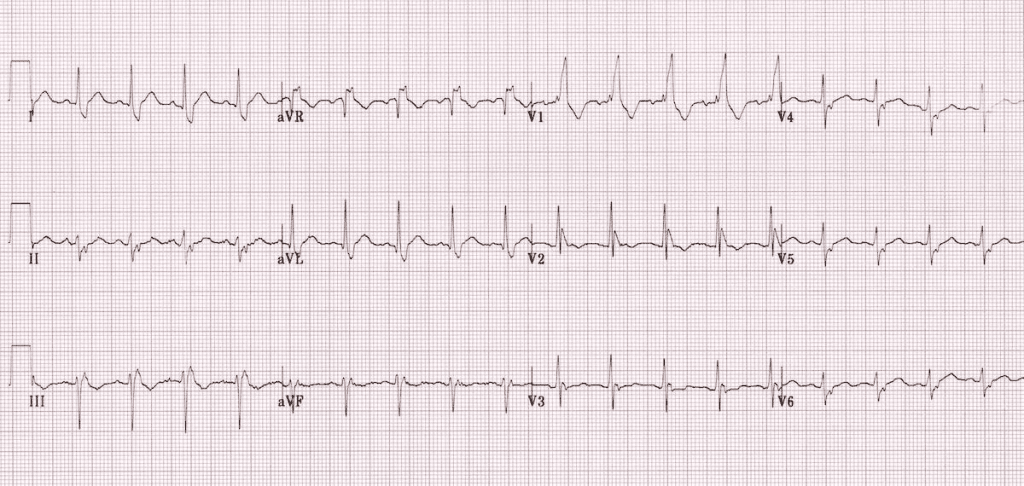
What is the diagnosis of ECG?
A. LBBB + LAFB
B. LBBB + LPFB
C. RBBB + LAFB
D. RBBB + LPFB
What is Bifascicular Block?
RBBB + LAFB is called Bifascicular Block ?
What are the types of bifascicular block [ECG patterns]?
- Right bundle branch block (RBBB) with left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) – left axis deviation (LAD)
- RBBB and left posterior fascicular block (LPFB) – right axis deviation (RAD) in the absence of other causes
| Bifascicular Block | ||
| 1 | RBBB + LAFB | More common |
| 2 | RBBB + LPFB | Less common |
Why RBBB + LAFB is more common than RBBB + LPFB in bifascicular block?
| Why commonest type of bifascicular block is RBBB + LAFB ? [ECG patterns] | Vulnerability to Damage |
| The LAF is supplied by a single branch of the left anterior descending artery (LAD). The LPF, on the other hand, receives a dual blood supply from both the right and left circumflex arteries. | Because the LAF has a single blood supply, it’s more susceptible to damage and block due to ischemia or other factors affecting the LAD. The LPF’s dual blood supply makes it more resistant to damage and block compared to the LAF. |
Anatomy and Blood Supply:
The LAF is supplied by a single branch of the left anterior descending artery (LAD).
The LPF, on the other hand, receives a dual blood supply from both the right and left circumflex arteries.
Vulnerability to Damage:
Because the LAF has a single blood supply, it’s more susceptible to damage and block due to ischemia or other factors affecting the LAD.
The LPF’s dual blood supply makes it more resistant to damage and block compared to the LAF.
Location and Relation to LV Outflow Tract:
The LAF’s location and relationship to the left ventricular (LV) outflow tract can also contribute to its vulnerability to damage, as it can be subjected to mechanical trauma.
Clinical Significance:
RBBB + LAFB is a common finding in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), and its presence can indicate underlying structural and electrical abnormalities.
RBBB + LPFB is less common and may be associated with more extensive underlying cardiac pathology.
| Blood supply | |||
| Left anterior fascicle (LAF) | More common for block | Single blood supply | LAD |
| Left posterior fascicle (LPF) | Less common for block | Dual blood supply | RCA + LCX |
Beck’s triad
Contents1 Beck’s triad2 Cause3 Pathophysiology4 Pathognomonic Beck’s triad Beck’s triad Cause Cause – associated with...
Beck’s triad [cardiology]
Contents1 Hypotension –2 Jugular venous distention (JVD)3 Muffled heart sounds Beck’s triad [cardiology]Components of Beck’s...
Bell’s palsy
Contents1 Most common cause of one-sided facial nerve paralysis –2 Bell’s palsy may present with...
Bence Jones protein
Contents1 Bence Jones protein2 Bence Jones protein mostly detected in3 Detection of Bence Jones protein...
Benign Lesions of the Cervix
Contents1 Cervical ectopy is a condition where the squamous epithelium of the ectocervix is replaced...
Berry’s ligament
Contents1 Berry’s ligament is the suspensory ligament of2 Berry’s ligament passes from the thyroid gland3...
Better outcomes after a catheter-based balloon mitral valvotomy procedure
Wilkins score of ——- predicts better outcomes after a catheter-based balloon mitral valvotomy procedure [A]...
Biotransformation
Contents1 Biotransformation is a metabolic process that takes place mainly in the2 Biotransformation helps to...
Birbeck granules
Birbeck granules Birbeck granules found in [A] Red pulp macrophages[B] Burr cells[C] Hofbauer cell[D] Langerhans...
Blast crisis
Blast crisis Blast crisis is the final phase in the evolution of CML,. In this...





