ECG Question-2
Contents
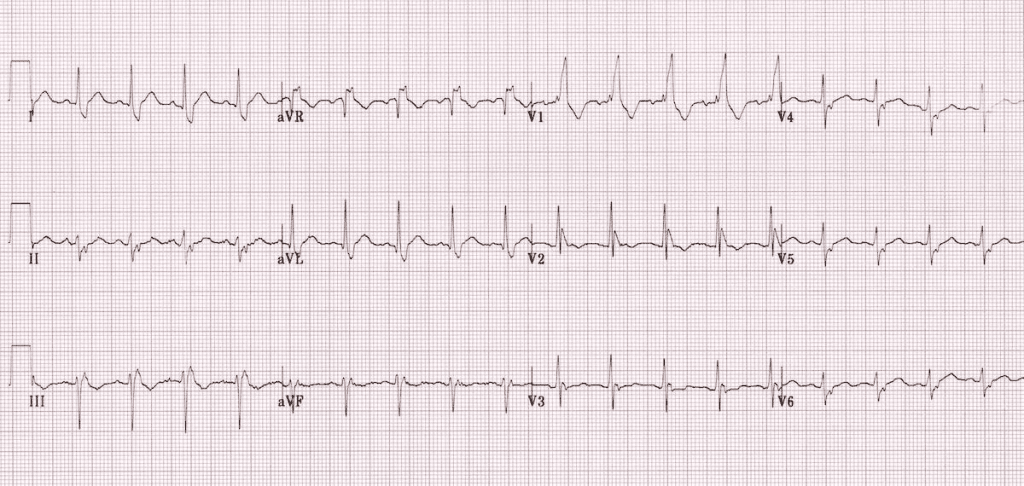
What is the diagnosis of ECG?
A. LBBB + LAFB
B. LBBB + LPFB
C. RBBB + LAFB
D. RBBB + LPFB
What is Bifascicular Block?
RBBB + LAFB is called Bifascicular Block ?
What are the types of bifascicular block [ECG patterns]?
- Right bundle branch block (RBBB) with left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) – left axis deviation (LAD)
- RBBB and left posterior fascicular block (LPFB) – right axis deviation (RAD) in the absence of other causes
| Bifascicular Block | ||
| 1 | RBBB + LAFB | More common |
| 2 | RBBB + LPFB | Less common |
Why RBBB + LAFB is more common than RBBB + LPFB in bifascicular block?
| Why commonest type of bifascicular block is RBBB + LAFB ? [ECG patterns] | Vulnerability to Damage |
| The LAF is supplied by a single branch of the left anterior descending artery (LAD). The LPF, on the other hand, receives a dual blood supply from both the right and left circumflex arteries. | Because the LAF has a single blood supply, it’s more susceptible to damage and block due to ischemia or other factors affecting the LAD. The LPF’s dual blood supply makes it more resistant to damage and block compared to the LAF. |
Anatomy and Blood Supply:
The LAF is supplied by a single branch of the left anterior descending artery (LAD).
The LPF, on the other hand, receives a dual blood supply from both the right and left circumflex arteries.
Vulnerability to Damage:
Because the LAF has a single blood supply, it’s more susceptible to damage and block due to ischemia or other factors affecting the LAD.
The LPF’s dual blood supply makes it more resistant to damage and block compared to the LAF.
Location and Relation to LV Outflow Tract:
The LAF’s location and relationship to the left ventricular (LV) outflow tract can also contribute to its vulnerability to damage, as it can be subjected to mechanical trauma.
Clinical Significance:
RBBB + LAFB is a common finding in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), and its presence can indicate underlying structural and electrical abnormalities.
RBBB + LPFB is less common and may be associated with more extensive underlying cardiac pathology.
| Blood supply | |||
| Left anterior fascicle (LAF) | More common for block | Single blood supply | LAD |
| Left posterior fascicle (LPF) | Less common for block | Dual blood supply | RCA + LCX |
Anatomy MCQs-2
Contents1 Largest organ in the human body2 Second Largest organ in the human body3 Smallest...
Anatomy MCQs-3
Contents1 Which divides the liver into a larger anatomical right lobe and a smaller anatomical...
Anatomy MCQs-4
Contents1 Each adult human kidney contains around ———– nephrons2 The kidneys receive approximately ————- of...
Anatomy MCQs-5
Contents1 During fetal life which is responsible for shunting a majority of blood flow of...
Anatomy of Skin
Contents1 Epidermis has ——- layers where the skin is thick2 In places of thin skin...
Anatomy of Tooth
Contents1 Ameloblasts are cells that deposit2 Odontoblasts produce3 Ameloblast are4 Secretory end of the ameloblast...
Ankle Fracture
Which structure is most commonly involved in ankle fracture ? Lateral malleolus What is the...
Ankle:Brachial Index
Contents1 What is Ankle Brachial Index?2 What is normal ABI?3 What is abnormal ABI?4 What...
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Contents1 Most common features of Ankylosing Spondylitis2 Most common extraarticular manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis3 Human...
Annihilation Coincidence Detection
Contents1 Annihilation Coincidence Detection2 Annihilation Coincidence Detection3 Mechanism Annihilation Coincidence Detection Annihilation Coincidence Detection Annihilation...





