ECG Question-2
Contents
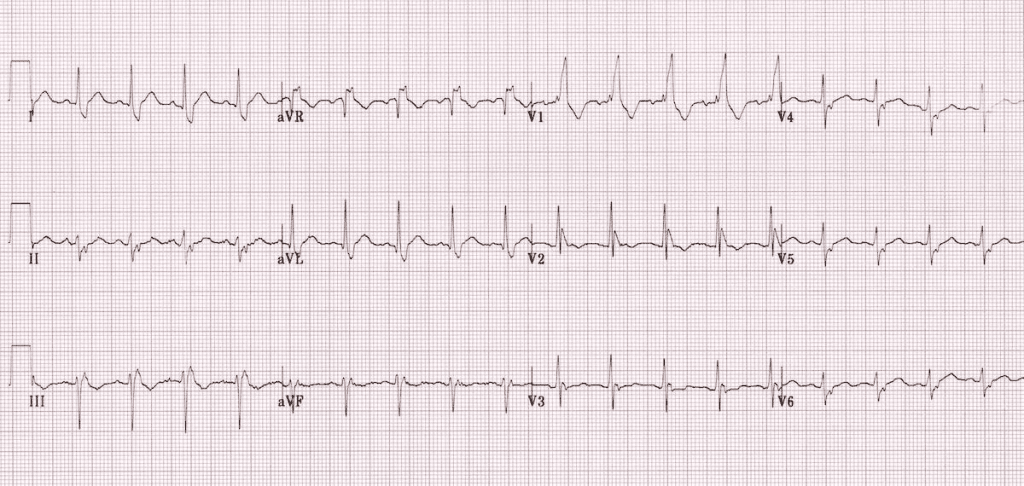
What is the diagnosis of ECG?
A. LBBB + LAFB
B. LBBB + LPFB
C. RBBB + LAFB
D. RBBB + LPFB
What is Bifascicular Block?
RBBB + LAFB is called Bifascicular Block ?
What are the types of bifascicular block [ECG patterns]?
- Right bundle branch block (RBBB) with left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) – left axis deviation (LAD)
- RBBB and left posterior fascicular block (LPFB) – right axis deviation (RAD) in the absence of other causes
| Bifascicular Block | ||
| 1 | RBBB + LAFB | More common |
| 2 | RBBB + LPFB | Less common |
Why RBBB + LAFB is more common than RBBB + LPFB in bifascicular block?
| Why commonest type of bifascicular block is RBBB + LAFB ? [ECG patterns] | Vulnerability to Damage |
| The LAF is supplied by a single branch of the left anterior descending artery (LAD). The LPF, on the other hand, receives a dual blood supply from both the right and left circumflex arteries. | Because the LAF has a single blood supply, it’s more susceptible to damage and block due to ischemia or other factors affecting the LAD. The LPF’s dual blood supply makes it more resistant to damage and block compared to the LAF. |
Anatomy and Blood Supply:
The LAF is supplied by a single branch of the left anterior descending artery (LAD).
The LPF, on the other hand, receives a dual blood supply from both the right and left circumflex arteries.
Vulnerability to Damage:
Because the LAF has a single blood supply, it’s more susceptible to damage and block due to ischemia or other factors affecting the LAD.
The LPF’s dual blood supply makes it more resistant to damage and block compared to the LAF.
Location and Relation to LV Outflow Tract:
The LAF’s location and relationship to the left ventricular (LV) outflow tract can also contribute to its vulnerability to damage, as it can be subjected to mechanical trauma.
Clinical Significance:
RBBB + LAFB is a common finding in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), and its presence can indicate underlying structural and electrical abnormalities.
RBBB + LPFB is less common and may be associated with more extensive underlying cardiac pathology.
| Blood supply | |||
| Left anterior fascicle (LAF) | More common for block | Single blood supply | LAD |
| Left posterior fascicle (LPF) | Less common for block | Dual blood supply | RCA + LCX |
Addison’s Plane
Anteriorly it passes through the tip of the 9th costal cartilage Posteriorly through the lower...
Adrenal Cortex
Contents1 Where is adrenal cortex situated?2 What are the Hormones secreted by Adrenal Cortex ?3 What...
After the PCI Procedure in Cath Lab: Femoral Sheaths should be removed in case of anticoagulation with heparin once the activated clotting time [ACT] is below
After the PCI Procedure in Cath Lab: Femoral Sheaths should be removed in case of...
Air crescent sign
What is ‘Air crescent sign’? Air crescent sign appears as a crescent of air surrounding...
Amaurosis Fugax
Contents1 Risk factors for amaurosis fugax include:2 Hollenhorst plaque3 Investigations Transient visual loss Amaurosis fugax is...
Ameloblast
Contents1 Ameloblasts form conical projections, known as Tomes’ processes in2 Tomes’s processes are those projections...
Amnestic Syndrome
Contents1 Amnestic syndrome refers to profound loss of2 Common presentation of Amnestic Syndrome3 Possible etiologies...
Amniotic Fluid Disorders
Contents1 All are causes of polyhydramnios except2 Following congenital anomalies can cause oligohydramnios except3 Not...
Anatomy MCQs-1
Contents1 All of the following are TRUE about Small Intestine EXCEPT2 Anatomic landmark that separates...





