ECG Question-2
Contents
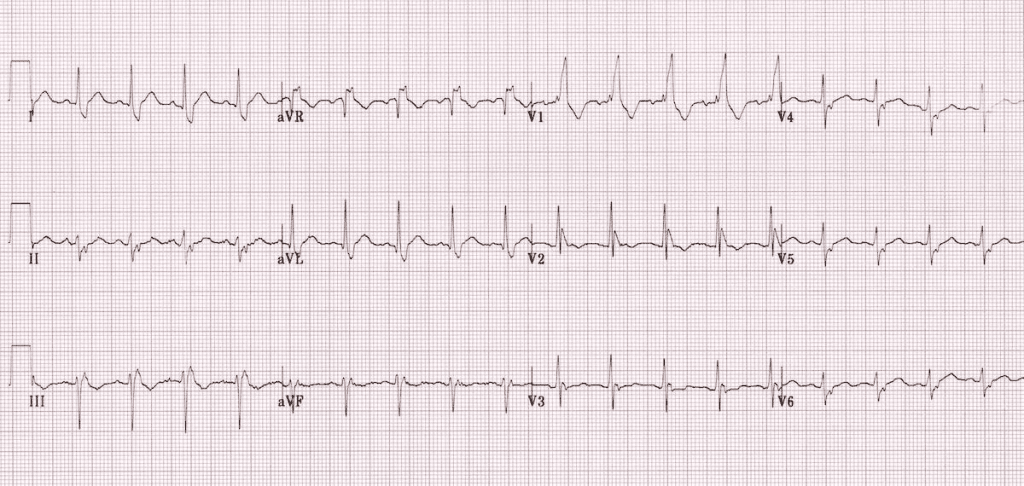
What is the diagnosis of ECG?
A. LBBB + LAFB
B. LBBB + LPFB
C. RBBB + LAFB
D. RBBB + LPFB
What is Bifascicular Block?
RBBB + LAFB is called Bifascicular Block ?
What are the types of bifascicular block [ECG patterns]?
- Right bundle branch block (RBBB) with left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) – left axis deviation (LAD)
- RBBB and left posterior fascicular block (LPFB) – right axis deviation (RAD) in the absence of other causes
| Bifascicular Block | ||
| 1 | RBBB + LAFB | More common |
| 2 | RBBB + LPFB | Less common |
Why RBBB + LAFB is more common than RBBB + LPFB in bifascicular block?
| Why commonest type of bifascicular block is RBBB + LAFB ? [ECG patterns] | Vulnerability to Damage |
| The LAF is supplied by a single branch of the left anterior descending artery (LAD). The LPF, on the other hand, receives a dual blood supply from both the right and left circumflex arteries. | Because the LAF has a single blood supply, it’s more susceptible to damage and block due to ischemia or other factors affecting the LAD. The LPF’s dual blood supply makes it more resistant to damage and block compared to the LAF. |
Anatomy and Blood Supply:
The LAF is supplied by a single branch of the left anterior descending artery (LAD).
The LPF, on the other hand, receives a dual blood supply from both the right and left circumflex arteries.
Vulnerability to Damage:
Because the LAF has a single blood supply, it’s more susceptible to damage and block due to ischemia or other factors affecting the LAD.
The LPF’s dual blood supply makes it more resistant to damage and block compared to the LAF.
Location and Relation to LV Outflow Tract:
The LAF’s location and relationship to the left ventricular (LV) outflow tract can also contribute to its vulnerability to damage, as it can be subjected to mechanical trauma.
Clinical Significance:
RBBB + LAFB is a common finding in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), and its presence can indicate underlying structural and electrical abnormalities.
RBBB + LPFB is less common and may be associated with more extensive underlying cardiac pathology.
| Blood supply | |||
| Left anterior fascicle (LAF) | More common for block | Single blood supply | LAD |
| Left posterior fascicle (LPF) | Less common for block | Dual blood supply | RCA + LCX |
Sebaceous glands
Contents1 All of the following are sebaceous glands except2 All are true regarding sebaceous glands...
A2-OS interval
Mitral Stenosis A2-OS interval Opening snap (OS) of the mitral stenosis is a high-pitched early...
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Contents1 Which of the following is implicated in dysfunctional uterine bleeding2 Anovulatory bleeding is excessive...
Abnormalities of placenta and cord
Contents1 Not true of placental anomalies is2 All are true of placenta accreta except3 Which...
Accessory pathway
Contents1 Most common sites for accessory pathways2 Mahaim pathways are typically seen on the3 Ventricular...
Acetaminophen & Hepatic injury
Blood levels of acetaminophen correlate with severity of hepatic injury
Acute appendicitis
Contents1 All are true of acute appendicitis except2 Not a feature of acute appendicitis3 In...
Acute liver failure
Contents1 Leading cause of acute liver failure in developing countries is2 Not commonly seen in...
Acute pancreatitis
Contents1 Most common causes of acute pancreatitis are2 The Atlanta classification broadly classifies acute pancreatitis...
Acute Pancreatitis Classification
Contents1 Atlanta classification2 Atlanta classification broadly classifies acute pancreatitis into two categories.3 Necrotizing pancreatitis (NP) which...





