ECG Question-1
Contents
- 1 What is the most probable diagnosis of ECG given below?
- 2 What is the mechanism of tenting of the T waves in hyperkalemia?
- 3 What is the mechanism of smaller P waves and widening of the QRS complex in hyperkalemia?
- 4 Peaked T waves in hyperkalemia are best seen in
- 5 What are the classic ECG changes associated with hyperkalemia?
- 6 What are the ECG findings associated with adverse outcomes?
- 7 Hyperkalemia severity –
What is the most probable diagnosis of ECG given below?
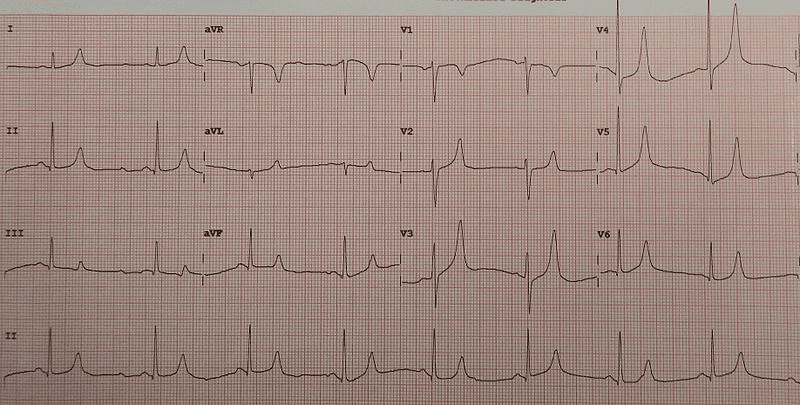
A. Hypercalcemia
B. Hyperkalemia
C. Hypocalcemia
D. Hypokalemia
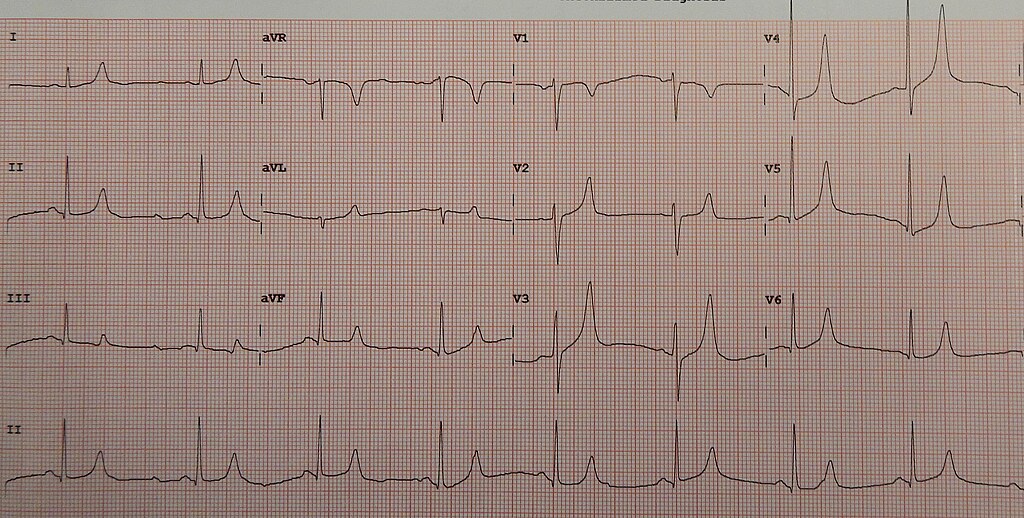
B. Hyperkalemia
C. Hypocalcemia
D. Hypokalemia

Mikael Häggström, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Mild to moderate hyperkalemia – prolongation of the PR interval and development of peaked T waves.
Severe hyperkalemia- widening of the QRS complex
What is the mechanism of tenting of the T waves in hyperkalemia?
A. Faster depolarisation
B. Slower repolarisation
C. Faster repolarisation
D. Slower repolarisation
What is the mechanism of smaller P waves and widening of the QRS complex in hyperkalemia?
A. Inactivation of potassium channels
B. Inactivation of sodium channels
C. Inactivation of calcium channels
D. Inactivation of Calcium-activated potassium channels
Peaked T waves in hyperkalemia are best seen in
A. Lead -I
B. Lead- II
C. aVF
D. Precordial leads
What are the classic ECG changes associated with hyperkalemia?
- Peaked T wave,
- Shortened QT interval,
- Lengthened PR interval,
- Increased QRS duration,
sine wave – absence of the P wave with the QRS complex seen as a ‘sine wave’.
What are the ECG findings associated with adverse outcomes?
Following ECG findings are associated with increased risk of adverse outcomes –
- Bradycardia,
- junctional rhythms
- QRS widening
Hyperkalemia severity –
| Degree of hyperkalaemia | Potassium level (mmol/L) | ||
| Mild | 5.3 – 6.0 | ||
| Moderate | 6.0 – 6.9 | ||
| Severe | ≥ 7.0 |




